U.S. Trucks Market Size & Share - Growth Forecast Report (2026-2035)
Industry Insight by Vehicle Type (Light-Duty Trucks, Heavy-Duty Trucks, Medium-Duty Trucks), by Application Type (Freight & Goods Transportation, Passenger or Dual-Purpose Deployment, Construction & Infrastructure Services, Specialised Operational Use), by End-User Industry (Transportation & Logistics Providers, Retail & Wholesale Distribution, Construction & Infrastructure Firms, Agriculture & Farming, Government & Public Services, Utilities / Energy Sector, Specialized Rental & Leasing Operators), by Fuel Type (Diesel Largest Segment, Electric Vehicles (BEV) Gasoline / Petrol, Hybrid Vehicles (HEV / PHEV), Alternative Fuels (CNG, LNG, Hydrogen)), by Payload (Light Payload, Extra Heavy Payload, Mid Payload, Heavy Payload)
| Status : Published | Published On : Feb, 2026 | Report Code : VRAT9669 | Industry : Automotive & Transportation | Available Format :

|
Page : 125 |
U.S. Trucks Market Size & Share - Growth Forecast Report (2026-2035)
Industry Insight by Vehicle Type (Light-Duty Trucks, Heavy-Duty Trucks, Medium-Duty Trucks), by Application Type (Freight & Goods Transportation, Passenger or Dual-Purpose Deployment, Construction & Infrastructure Services, Specialised Operational Use), by End-User Industry (Transportation & Logistics Providers, Retail & Wholesale Distribution, Construction & Infrastructure Firms, Agriculture & Farming, Government & Public Services, Utilities / Energy Sector, Specialized Rental & Leasing Operators), by Fuel Type (Diesel Largest Segment, Electric Vehicles (BEV) Gasoline / Petrol, Hybrid Vehicles (HEV / PHEV), Alternative Fuels (CNG, LNG, Hydrogen)), by Payload (Light Payload, Extra Heavy Payload, Mid Payload, Heavy Payload)
U.S. Trucks Market Overview
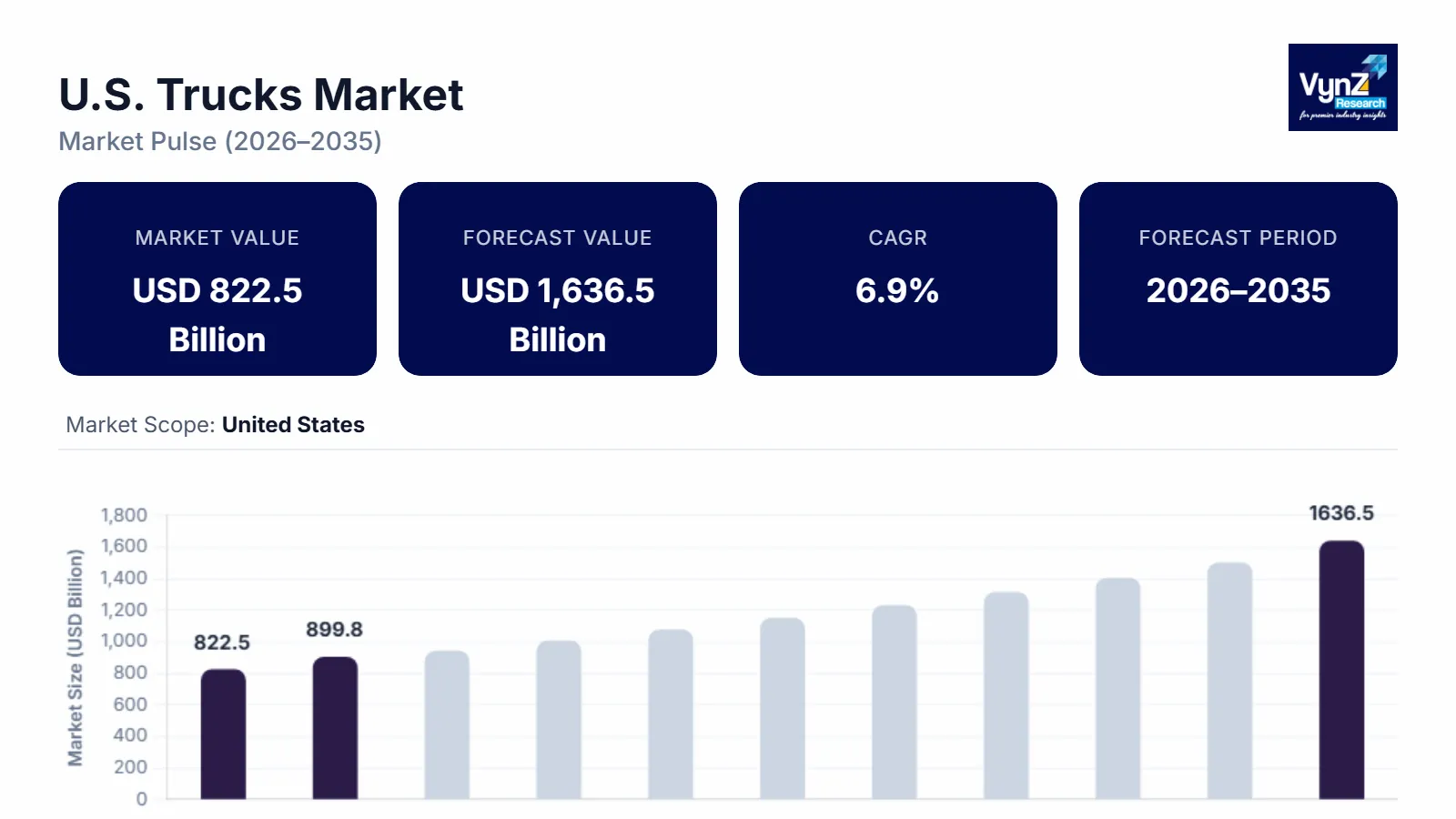
The U.S. trucks market, which was valued at approximately USD 822.5 billion in 2025 and is estimated to reach around USD 899.8 billion in 2026, is projected to reach close to USD 1,636.5 billion by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of about 6.9% during the forecast period from 2026 to 2035.
The U.S. trucking industry is growing rapidly because trucking has become a backbone of American commerce; logistics and industrial activity, providing the ability to move goods throughout retail, manufacturing, construction, agricultural, and energy industries. Rapid growth in e-commerce, changes to the way that companies operate their supply chain, and rapid growth in time-sensitive distribution of goods have created a need for trucking fleets to be able to provide reliable, safe, and efficient freight service and last-mile delivery.
At the same time, fleet owners/operators continue to update their equipment to increase its reliability, safety, and downtime potential as the operating environment becomes increasingly complex. In addition, regulatory pressures and investments in new infrastructure will continue to drive the use of more advanced, connected, and sustainable technology, such as advanced powertrains and advanced connectivity solutions, to further position trucks as critical platforms to support both digitally-enabled and low-emission logistics and productivity activities across various types of operating environments, as trucks transported 11.27 billion tons of freight in 2024, reinforcing their role as the primary mover of domestic cargo.
U.S. Trucks Market Dynamics
Market Trends
The trucking industry has experienced an enormous transition from a physical fleet of trucks to a technology-based model of logistics and operations. This transition is due to increased use of technology in the form of digital integration and connectivity, as well as the use of automation in all aspects of the operation. Truck fleets are using advanced telematics, predictive maintenance, and AI to route their equipment for optimal usage at the lowest cost possible, especially with changes in freight demand and increasing pressure on profit margins. Additionally, there is a growing interest in electric and alternative power source options, which will be used to transform product offerings and environmental sustainability targets for fleets. In addition, the developments of autonomous vehicles, networking capabilities, and new subscription services indicate a larger trend of moving away from the traditional asset-based business model and towards a service-based business model that utilizes data to create more efficient, resilient, and responsive transportation solutions for customers, as According to the International Energy Agency, global sales of electric heavy-duty trucks exceeded 90,000 units in 2024, reflecting rapid adoption of sustainable freight technologies.
Growth Drivers
The market is also influenced by the increased reliance on e-commerce and freight demand, which has increased trucking as the mainstay logistics provider for all forms of last-mile delivery (e.g., direct-to-consumer), omnichannel retail fulfilment, and intercity distribution networks. The increase in demand for freight movement is supported by changing consumer purchasing habits and increasing expectations for faster, reliable, and responsive supply chains. In addition, parallel investment in transportation infrastructure and new or upgraded equipment will support greater efficiency and capacity within operations, supporting operators to both grow and upgrade their fleets, as According to the International Air Transport Association, global air cargo demand increased by 11.3% in 2024, amplifying pressure on intermodal logistics and trucking capacity.
Market Restraints / Challenges
The industry has a number of operational, workforce, and regulatory limitations that limit the industry's full capability to operate. There is a long-standing shortage of skilled drivers, and workforce shortages are also reducing fleet size and the reliability of services provided by fleets as they face the growing age of their current employee base and increasing difficulties with recruiting new employees. The volatility of fuel prices and the rapidly increasing operating expense of fleet operations are causing increasing economic pressures on carriers, particularly for the smaller carriers. Delays in semiconductor deliveries and delays in the supply of other raw materials are continuing to disrupt the manufacturing and delivery process of products. In addition, there will be increased complexities and costs associated with environmental and safety regulations, and this will require substantial investment in technologies, training, and upgrades to fleets, which may reduce growth opportunities and encourage the carriers to continue to expand operations.
Market Opportunities
The trucking industry has a lot of opportunities available due to the changes in technology and the growing demands in logistics. The expanding use of electric and alternative-fueled trucks is being driven by the increasing number of regulations to limit greenhouse gas emissions, as well as companies' commitment to reducing their carbon footprint. There are also advances in the development of autonomous vehicles and connected vehicle platforms that could help increase safety and make it easier to find drivers, while at the same time improving the efficiency of fleets. As well, the continued growth in e-commerce and last-mile delivery will continue to create the need for companies to develop new logistics and supply chain solutions using digital platforms and real-time information to improve their ability to operate efficiently and respond quickly to customers.
U.S. Trucks Market Report Coverage
|
Report Metric |
Details |
|
Historical Period |
2020 - 2024 |
|
Base Year Considered |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026 - 2035 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 822.5 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast in 2035 |
USD 636.5 Billion |
|
Growth Rate |
6.9% |
|
Segments Covered in the Report |
Vehicle Type, Application Type, End-User Industry, Fuel Type, Payload, |
|
Report Scope |
Market Trends, Drivers, and Restraints; Revenue Estimation and Forecast; Segmentation Analysis; Companies’ Strategic Developments; Market Share Analysis of Key Players; Company Profiling |
|
Regions Covered in the Report |
Western, Southern |
|
Key Companies |
Ford Motor Company, General Motors, PACCAR Inc., Daimler Truck North America, Volvo Group, Navistar International, Tesla, Inc., Rivian Automotive, Inc., Schneider National, Inc., UPS Inc., FedEx Corp., Knight‑Swift Transportation Holdings, XPO Inc., Penske Truck Leasing Co., L.P., Werner Enterprises, Inc. |
|
Customization |
Available upon request |
U.S. Trucks Market Segmentation
By Vehicle Type
Light-duty trucks are estimated to account for approximately 65% of total market revenue in 2025. This is due to their ability to be used in commercial, municipal, and personal use situations. Light-duty trucks are important for last-mile logistics, service fleets, small business operations, and support a favourable operating economy. The light-duty truck is well-suited for the urban environment and has availability across most original equipment manufacturer (OEM) portfolios. The versatility of the light-duty truck supports a sustained procurement model based on its diverse duty cycles and rapid replacement cycles, further supporting its position as the leading type of vehicle in overall fleet composition.
Heavy-duty trucks are expanding rapidly with a growth rate of 7.2% during the forecast period, due to an increase in freight and a focus on high-capacity, long-haul transportation by logistics companies. The need for large payloads is also being driven by network design, regional distribution centres, and industrial development tied to infrastructure improvements. Modernizing fleets through new vehicles combined with investments in improved safety and powertrain technology will continue to drive rapid replacement and expansion of heavy-duty vehicle sales, as According to the International Energy Agency, global sales of electric heavy-duty trucks exceeded 90,000 units in 2024, highlighting accelerated fleet modernization.
By Application Type
Freight & goods transportation dominate the market with a share of around 60% in 2025. This is associated with the primary use of trucks today primarily because of the importance that trucking plays within the country's economy and its ability to provide a continuous supply chain. Additionally, the strong reliance by businesses on road-based logistics systems (intercity freight, regional distribution, last mile) will continue to maintain very high usage levels. As such, companies will have to continually rely on dependable capacity in the transportation sector as this is necessary to support their inventory levels and service level commitments while also providing timely deliveries throughout retail and industrial value chains, as trucks transported 11.27 billion tons of freight in 2024, underscoring the scale of freight dependency on road transport.
Dual-purpose usage is growing due to the dual purpose of being a personal vehicle for consumers and small business owners; with the added benefit of a vehicle with cargo capabilities. The increase of contractors, flexible work models and lifestyle driven purchasing has also created an additional need for versatile trucks which can be used for daily mobility and occasional light commercial tasks. OEM product strategy is now increasingly focused on the blending of utility and personal vehicle usage.
By End-User Industry
Transportation and logistics providers held the largest market share of about 35% in 2025. This is because trucking is a key component in freight movement, distribution networks, and service reliability. Fleet renewal on an ongoing basis is required to maintain uptime, meet service level agreements, and manage operational risk. Sustained purchasing volumes across operating cycles through scale-driven procurement and professional fleet management practices support consistent volume buying.
Retail and wholesale distribution are experiencing a surge in growth as omnichannel retail has created new challenges and opportunities for how products are fulfilled. As a result of these challenges and opportunities, distributors are using flexible trucking capacity in their supply chain to fulfil their customers’ need for fast replenishment of stock, to move stock to decentralised warehouse locations, and to meet customer-centric delivery expectations. The desire for fast cycle times for orders and the need to have inventory closer to customers are fueling a need for fleet expansion and specialisation at the end-user level, as U.S. parcel volumes reached 22.37 billion shipments in 2024, reflecting continued pressure on delivery networks.
By Fuel Type
Diesel dominates the market with a share of approx. 70% in 2025. This is because of its reliability with heavy payloads, in long-haul operation, and in a high-utilisation duty cycle. The existing fueling infrastructure, consistent performance in varying operating environments, and strong resale values provide fleets with a reason to favour diesel. In addition to offering fleet operators the potential for higher reliability and operational continuity at scale for mission-critical logistics operations, diesel powertrain solutions also provide the option for operators to maintain a level of control over their logistics operations.
Electric trucks have become the fastest-growing segment of electric vehicles with a CAGR of 7.4% in the coming years, as companies begin to use them for their fleet operations. Fleet operations are finding that electric trucks will allow them to both decarbonize their fleets and improve the operational efficiency of their fleets while complying with increasing urban and regional emission regulations. The growth of electric trucks is being driven by advancements in charging ecosystems that provide reliable and convenient access to charging locations for fleet operators. Additionally, vehicle manufacturers are continuing to enhance the range of electric trucks, making them increasingly suitable for use on fixed and predictable routes that fleet operators can rely upon, as According to the International Energy Agency, global electric heavy-duty truck sales exceeded 90,000 units in 2024.
By Payload
Due to the widespread presence of lightweight payload class vehicles in service fleets, urban logistics, and small businesses, they are a leading cause for new vehicle sales. They are ideal for short-haul delivery and service work because of their low operating costs, simplicity of operation, and low maintenance requirements, which provide an advantage for last-mile and service-based delivery models. The high volume of new vehicle sales, as well as the variety of uses that lightweight class vehicles support, also continue to be a strong driver of demand.
Heavy payload classes are rapidly growing at a CAGR of about 7.8% during the forecast period, as consolidation of freight, long-haul efficiency goals and industrial logistics demand higher capacity transportation. Rationale for network rationalization is focusing on fewer vehicles with higher capacities to maximize throughput and asset use. Increased investments in advanced safety solutions, connectivity solutions and power train solutions are also increasing fleet upgrades in this category.
Regional Insights
U.S. Trucks Market
The U.S. trucking industry is a complex system with many different parts (i.e., inland logistics demand, trade, and regional economies). Trucking is used to move goods all over the country for retailers, manufacturers, and agricultural industries. Reliability and capacity are improved through investments in infrastructure, intermodal shipping facilities, and technologies such as tracking systems and electronic logs. Cross-border trade also supports the long-haul freight market. Additionally, there are regional differences based on the location of ports, inland distribution centres, and areas with specialised industry, which create different operating characteristics that affect how fleets operate and how they should be designed for each region in the United States.
Western United States Trucks Market
The West region is growing through the expansion of ports, industrial diversity, and infrastructure to extend freight corridors and urban distribution networks. Through geographic size and intermodal connections, demand exists for both heavy-duty trucks and versatile trucking platforms to drive demand for western regional growth, as According to the Port of Los Angeles, container throughput reached 10.3 million TEUs in 2024, sustaining high regional freight movement.
Southern United States Trucks Market
The southern part of the United States is responsible for the highest market share because of a strong industrial base, large numbers of ports that allow for transportation via water, and an increasing number of distribution centres. The continued growth in the construction, agricultural, and freight industries, along with logistics systems that are strategically located throughout the South, will continue to sustain high levels of trucking demand, solidifying its position as the biggest share of the overall trucking market in the United States.
Competitive Landscape / Company Insights
Mini Profiles
Ford Motor Company continues to be a key player in the U.S. trucks market with its light-duty and commercial trucks, serving fleet operators, logistics providers, and individual customers, alongside the broader Ford automotive ecosystem.
General Motors remains a major force in the U.S. truck industry, producing light- and medium-duty trucks for commercial, industrial, and consumer markets, along with connected mobility solutions across the GM brand portfolio.
PACCAR Inc. continues to serve the global truck market through its Kenworth, Peterbilt, and DAF brands, providing medium- and heavy-duty trucks for freight, construction, and logistics, complemented by innovative powertrain and telematics offerings.
Daimler Truck North America maintains its presence with Freightliner and Western Star trucks, supplying heavy-duty and vocational vehicles for long-haul, industrial, and fleet operators, while integrating advanced safety and efficiency technologies.
Volvo Group continues to support the freight, construction, and logistics sectors with heavy-duty trucks and industrial vehicles, emphasising reliability, sustainable powertrains, and global operational support across its brands.
Key Players
- Ford Motor Company
- General Motors
- PACCAR Inc.
- Daimler Truck North America
- Volvo Group
- Navistar International
- Tesla, Inc.
- Rivian Automotive, Inc.
- Schneider National, Inc.
- UPS Inc.
- FedEx Corp.
- Knight ‑ Swift Transportation Holdings
- XPO Inc.
- Penske Truck Leasing Co., L.P.
- Werner Enterprises, Inc.
Recent Developments
January 2026 - Oshkosh Defence issued a recall of select Next Generation Delivery Vehicles after a manufacturing defect was identified in the rear wheel assembly of USPS mail carrier trucks, prompting safety corrective action.
January 2026 - Volvo Trucks was reported as leading the heavy truck market position in Europe, reflecting competitive positioning and delivery momentum across global markets.
December 2025 - 10 Roads Express announced it would cease operations by January 30, 2026, ending nearly five decades of mail haul service due to shifting network dynamics.
November 2025 - the USPS unveiled the Next Generation Delivery Vehicle (NGDV) built by Oshkosh Corporation, marking the deployment of updated mail trucks with modern features to replace ageing vehicles.
October 2025 - Aurora Innovation confirmed plans to operate hundreds of commercial autonomous trucks across U.S. Sun Belt corridors by the end of 2026, maintaining progress in driverless freight deployment.
U.S. Trucks Market Coverage
Vehicle Type Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- Light-Duty Trucks
- Heavy-Duty Trucks
- Medium-Duty Trucks
Application Type Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- Freight & Goods Transportation
- Passenger or Dual-Purpose Deployment
- Construction & Infrastructure Services
- Specialised Operational Use
End-User Industry Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- Transportation & Logistics Providers
- Retail & Wholesale Distribution
- Construction & Infrastructure Firms
- Agriculture & Farming
- Government & Public Services
- Utilities / Energy Sector
- Specialized Rental & Leasing Operators
Fuel Type Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- Diesel Largest Segment
- Electric Vehicles (BEV) Gasoline / Petrol
- Hybrid Vehicles (HEV / PHEV)
- Alternative Fuels (CNG
- LNG
- Hydrogen)
Payload Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- Light Payload
- Extra Heavy Payload
- Mid Payload
- Heavy Payload
U.S. Trucks Market by Region
- Western
- By Vehicle Type
- By Application Type
- By End-User Industry
- By Fuel Type
- By Payload
- Southern
- By Vehicle Type
- By Application Type
- By End-User Industry
- By Fuel Type
- By Payload
Table of Contents for U.S. Trucks Market Report
1. Research Overview
1.1. The Report Offers
1.2. Market Coverage
1.2.1. By
Vehicle Type
1.2.2. By
Application Type
1.2.3. By
End-User Industry
1.2.4. By
Fuel Type
1.2.5. By
Payload
1.3. Research Phases
1.4. Limitations
1.5. Market Methodology
1.5.1. Data Sources
1.5.1.1.
Primary Research
1.5.1.2.
Secondary Research
1.5.2. Methodology
1.5.2.1.
Data Exploration
1.5.2.2.
Forecast Parameters
1.5.2.3.
Data Validation
1.5.2.4.
Assumptions
1.5.3. Study Period & Data Reporting Unit
2. Executive Summary
3. Industry Overview
3.1. Industry Dynamics
3.1.1. Market Growth Drivers
3.1.2. Market Restraints
3.1.3. Key Market Trends
3.1.4. Major Opportunities
3.2. Industry Ecosystem
3.2.1. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
3.2.2. Recent Development Analysis
3.2.3. Value Chain Analysis
3.3. Competitive Insight
3.3.1. Competitive Position of Industry
Players
3.3.2. Market Attractive Analysis
3.3.3. Market Share Analysis
4. U.S. Market Estimate and Forecast
4.1. U.S. Market Overview
4.2. U.S. Market Estimate and Forecast to 2035
5. Market Segmentation Estimate and Forecast
5.1. By Vehicle Type
5.1.1. Light-Duty Trucks
5.1.1.1. Market Definition
5.1.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.1.2. Heavy-Duty Trucks
5.1.2.1. Market Definition
5.1.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.1.3. Medium-Duty Trucks
5.1.3.1. Market Definition
5.1.3.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.2. By Application Type
5.2.1. Freight & Goods Transportation
5.2.1.1. Market Definition
5.2.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.2.2. Passenger or Dual-Purpose Deployment
5.2.2.1. Market Definition
5.2.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.2.3. Construction & Infrastructure Services
5.2.3.1. Market Definition
5.2.3.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.2.4. Specialised Operational Use
5.2.4.1. Market Definition
5.2.4.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.3. By End-User Industry
5.3.1. Transportation & Logistics Providers
5.3.1.1. Market Definition
5.3.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.3.2. Retail & Wholesale Distribution
5.3.2.1. Market Definition
5.3.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.3.3. Construction & Infrastructure Firms
5.3.3.1. Market Definition
5.3.3.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.3.4. Agriculture & Farming
5.3.4.1. Market Definition
5.3.4.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.3.5. Government & Public Services
5.3.5.1. Market Definition
5.3.5.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.3.6. Utilities / Energy Sector
5.3.6.1. Market Definition
5.3.6.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.3.7. Specialized Rental & Leasing Operators
5.3.7.1. Market Definition
5.3.7.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.4. By Fuel Type
5.4.1. Diesel Largest Segment
5.4.1.1. Market Definition
5.4.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.4.2. Electric Vehicles (BEV) Gasoline / Petrol
5.4.2.1. Market Definition
5.4.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.4.3. Hybrid Vehicles (HEV / PHEV)
5.4.3.1. Market Definition
5.4.3.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.4.4. Alternative Fuels (CNG
5.4.4.1. Market Definition
5.4.4.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.4.5. LNG
5.4.5.1. Market Definition
5.4.5.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.4.6. Hydrogen)
5.4.6.1. Market Definition
5.4.6.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.5. By Payload
5.5.1. Light Payload
5.5.1.1. Market Definition
5.5.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.5.2. Extra Heavy Payload
5.5.2.1. Market Definition
5.5.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.5.3. Mid Payload
5.5.3.1. Market Definition
5.5.3.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.5.4. Heavy Payload
5.5.4.1. Market Definition
5.5.4.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
6. Western Market Estimate and Forecast
6.1. By
Vehicle Type
6.2. By
Application Type
6.3. By
End-User Industry
6.4. By
Fuel Type
6.5. By
Payload
7. Southern Market Estimate and Forecast
7.1. By
Vehicle Type
7.2. By
Application Type
7.3. By
End-User Industry
7.4. By
Fuel Type
7.5. By
Payload
8. Company Profiles
8.1.
Ford Motor Company
8.1.1.
Snapshot
8.1.2.
Overview
8.1.3.
Offerings
8.1.4.
Financial
Insight
8.1.5.
Recent
Developments
8.2.
General Motors
8.2.1.
Snapshot
8.2.2.
Overview
8.2.3.
Offerings
8.2.4.
Financial
Insight
8.2.5.
Recent
Developments
8.3.
PACCAR Inc.
8.3.1.
Snapshot
8.3.2.
Overview
8.3.3.
Offerings
8.3.4.
Financial
Insight
8.3.5.
Recent
Developments
8.4.
Daimler Truck North America
8.4.1.
Snapshot
8.4.2.
Overview
8.4.3.
Offerings
8.4.4.
Financial
Insight
8.4.5.
Recent
Developments
8.5.
Volvo Group
8.5.1.
Snapshot
8.5.2.
Overview
8.5.3.
Offerings
8.5.4.
Financial
Insight
8.5.5.
Recent
Developments
8.6.
Navistar International
8.6.1.
Snapshot
8.6.2.
Overview
8.6.3.
Offerings
8.6.4.
Financial
Insight
8.6.5.
Recent
Developments
8.7.
Tesla, Inc.
8.7.1.
Snapshot
8.7.2.
Overview
8.7.3.
Offerings
8.7.4.
Financial
Insight
8.7.5.
Recent
Developments
8.8.
Rivian Automotive, Inc.
8.8.1.
Snapshot
8.8.2.
Overview
8.8.3.
Offerings
8.8.4.
Financial
Insight
8.8.5.
Recent
Developments
8.9.
Schneider National, Inc.
8.9.1.
Snapshot
8.9.2.
Overview
8.9.3.
Offerings
8.9.4.
Financial
Insight
8.9.5.
Recent
Developments
8.10.
UPS Inc.
8.10.1.
Snapshot
8.10.2.
Overview
8.10.3.
Offerings
8.10.4.
Financial
Insight
8.10.5.
Recent
Developments
8.11.
FedEx Corp.
8.11.1.
Snapshot
8.11.2.
Overview
8.11.3.
Offerings
8.11.4.
Financial
Insight
8.11.5.
Recent
Developments
8.12.
Knight-Swift Transportation Holdings
8.12.1.
Snapshot
8.12.2.
Overview
8.12.3.
Offerings
8.12.4.
Financial
Insight
8.12.5.
Recent
Developments
8.13.
XPO Inc.
8.13.1.
Snapshot
8.13.2.
Overview
8.13.3.
Offerings
8.13.4.
Financial
Insight
8.13.5.
Recent
Developments
8.14.
Penske Truck Leasing Co., L.P.
8.14.1.
Snapshot
8.14.2.
Overview
8.14.3.
Offerings
8.14.4.
Financial
Insight
8.14.5.
Recent
Developments
8.15.
Werner Enterprises, Inc.
8.15.1.
Snapshot
8.15.2.
Overview
8.15.3.
Offerings
8.15.4.
Financial
Insight
8.15.5.
Recent
Developments
9. Appendix
9.1. Exchange Rates
9.2. Abbreviations
Note: Financial insight and recent developments of different companies are subject to the availability of information in the secondary domain.
Frequently Asked Questions
Purchase Options
Latest Report
Research Methodology
- Desk Research / Pilot Interviews
- Build Market Size Model
- Research and Analysis
- Final Deliverable
Connect With Our Sales Team
- Toll-Free: +1-888-253-3960
- Phone: +91 9960 288 381
- Email: enquiry@vynzresearch.com
U.S. Trucks Market
