Smart Building Market Size & Share - Growth Forecast Report (2026-2035)
Industry Insight by Component (Solutions, Services), by Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial)
| Status : Published | Published On : Feb, 2026 | Report Code : VRCH2125 | Industry : Chemicals & Materials | Available Format :

|
Page : 190 |
Smart Building Market Size & Share - Growth Forecast Report (2026-2035)
Industry Insight by Component (Solutions, Services), by Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial)
Smart Building Market Overview
The smart building market which was valued at approximately USD 140.6 billion in 2025 and is estimated to reach around USD 177.2 billion in 2026, is projected to reach close to USD 844.5 billion by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of about 18.9% during the forecast period from 2026 to 2035.
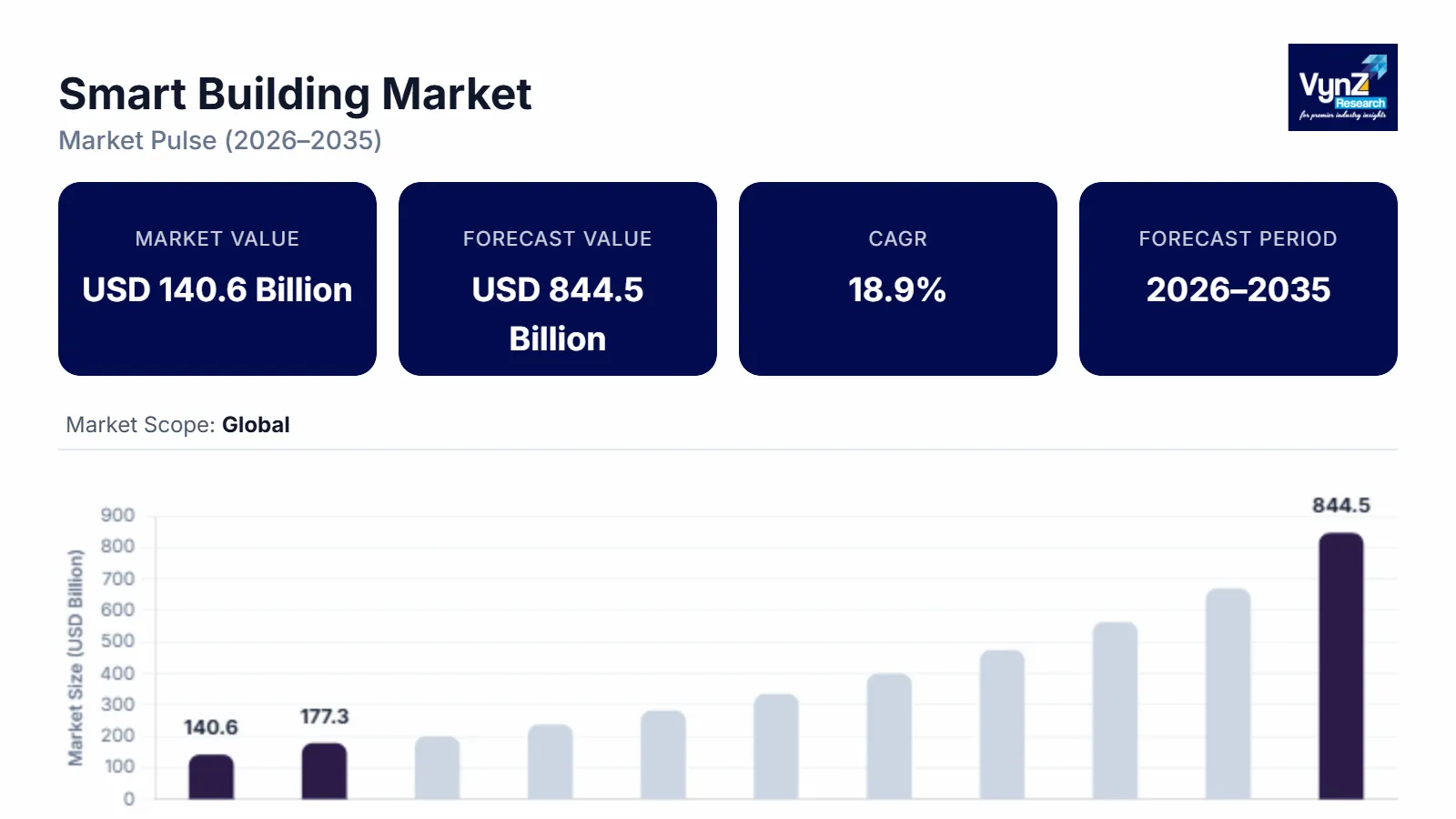
The market is expanding as real estate owners, enterprises, and governments redefine buildings as strategic, data-driven assets rather than static infrastructure. Escalating energy costs, sustainability commitments, and regulatory pressure are compelling organizations to adopt intelligent systems that continuously optimize energy usage, safety, and operational efficiency.
In parallel, rapid advances in IoT, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence are enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and centralized control across increasingly complex building environments. Occupants now expect healthier, safer, and more personalized spaces, pushing building operators to invest in technologies that enhance comfort and productivity while reducing risk. From an investment perspective, smart buildings deliver measurable value by extending asset life, improving compliance, lowering operating expenses, and strengthening long-term property valuations. As a result, smart building solutions are no longer discretionary enhancements but core infrastructure investments, driving sustained demand across residential, commercial, and institutional sectors worldwide.
Market Dynamics
Market Trends
Smart buildings are increasingly defined by sustainability and energy performance standards as governments strengthen regulations and energy codes. For example, the Indian government’s Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) Star Rating Programme has awarded multiple five-star ratings to government infrastructure projects, including Paryavaran Bhawan, which achieved net-zero electrical consumption with integrated solar generation—a benchmark of efficient public building performance. Similarly, Andhra Pradesh leads India in implementing the Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC), with hundreds of buildings meeting minimum energy performance standards established by the Union government to reduce electricity demand in commercial structures. These initiatives reflect a broader global trajectory toward regulatory frameworks that mandate or incentivize intelligent, digitally controlled energy systems, accelerating the adoption of building automation and energy analytics across sectors.
Growth Drivers
One of the most powerful drivers of smart building adoption is the urgent need to reduce energy consumption and emissions from the built environment. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the operations of buildings account for about 30 % of global final energy use and a similar share of energy-related carbon emissions, making buildings a focal point for decarbonisation strategies. As governments tighten building performance standards and align with climate goals, organisations increasingly invest in integrated sensors, automation, and analytics that optimise HVAC, lighting, and energy flows in real time. These technologies not only support compliance with environmental regulations but also enable building owners to demonstrate measurable progress toward national emissions reduction commitments, strengthening corporate sustainability reporting and unlocking potential incentives tied to energy performance.
Market Restraints / Challenges
Despite its potential, the smart building market faces implementation barriers rooted in cost, complexity, and skills gaps. Transitioning existing building stock to intelligent operations often requires substantial upfront investment in IoT sensors, building automation systems, and integration platforms. Compounding this, many jurisdictions still lack harmonised standards for data exchange and performance measurement, making interoperability among different systems a persistent challenge. Moreover, energy efficiency initiatives must be supported by policy frameworks and funding mechanisms that make technology adoption financially viable for smaller organisations and public sector owners. Without clear government incentives or financing programmes, some owners delay upgrades due to capital constraints or uncertainty about long-term returns. Thus, aligning policy support with capacity building and financing solutions remains critical to unlocking broader adoption across diverse building portfolios.
Market Opportunities
Smart buildings present a compelling opportunity to align economic performance with sustainability outcomes, especially as public sector programmes prioritise efficient infrastructure. Beyond operational cost savings, intelligent building technologies enable real-time energy monitoring and demand response capabilities that support grid stability and peak load management. Governments are increasingly recognising this value: public investments in energy upgrades for schools, hospitals, and community buildings—such as the UK’s multi-hundred-million-pound clean energy retrofit programme—aim to reduce long-term energy costs while advancing national climate commitments. Additionally, smart building analytics can help organisations meet targets under energy efficiency and carbon reduction frameworks, creating opportunities for performance-based contracts, green financing, and asset value enhancement. As the regulatory landscape evolves toward stricter efficiency requirements, early adopters of smart building technologies will be positioned to capture both regulatory incentives and competitive differentiation.
Global Smart Building Market Report Coverage
|
Report Metric |
Details |
|
Historical Period |
2020 - 2024 |
|
Base Year Considered |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026 - 2035 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 140.6 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast in 2035 |
USD 844.5 Billion |
|
Growth Rate |
18.9% |
|
Segments Covered in the Report |
Component, Application |
|
Report Scope |
Market Trends, Drivers, and Restraints; Revenue Estimation and Forecast; Segmentation Analysis; Companies’ Strategic Developments; Market Share Analysis of Key Players; Company Profiling |
|
Regions Covered in the Report |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Rest of the World |
|
Key Companies |
Honeywell International Inc., Siemens AG, Schneider Electric SE, Johnson Controls International plc, ABB Ltd., Cisco Systems, Inc., Hitachi, Ltd., IBM Corporation, Intel Corporation, Legrand SA, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., amd Emerson Electric Co. |
|
Customization |
Available upon request |
Market Segmentation
By Component
Solutions represent the largest component category, with a market share of around 70% in 2025, because they form the core digital and physical infrastructure required to meet national energy, safety, and performance mandates. Governments increasingly regulate building operations through technology-enabled standards rather than manual processes. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, buildings account for approximately 76% of total U.S. electricity consumption, underscoring why energy management, automation, and control solutions are central to policy objectives. In Europe, the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive requires new buildings to be zero-emission by 2030, directly accelerating adoption of building automation, energy management systems, and digital controls. As compliance, efficiency, and sustainability become non-negotiable, solutions remain the dominant investment focus across residential, commercial, and public infrastructure projects.
There Solutions further classified into followings
- Energy Management Solutions
- Building Infrastructure Management Solutions
- Safety & Security Solutions
- Network & Workplace Management Solutions
Services are the fastest-growing component category with a CAGR of 19.2% in the coming years, as building owners worldwide transition from one-time technology deployment to continuous performance management and optimization. Across global markets, governments are increasingly emphasizing lifecycle efficiency, operational accountability, and verified outcomes rather than static, design-stage compliance. International policy frameworks, such as those promoted by the European Union, encourage the use of energy performance contracting models, where efficiency gains are measured and sustained over time, often through specialized service partners. This shift reinforces the need for ongoing monitoring, analytics, optimization, and compliance support throughout a building’s operational life. As smart buildings evolve into continuously operated digital assets, owners recognize that long-term value depends on expert services that ensure systems perform as intended. These dynamics are accelerating global demand for managed services and performance-based support.
There Services further classified into followings
- System Integration & Deployment
- Consulting & Design
- Support & Maintenance
- Managed Services
- Training & Optimization
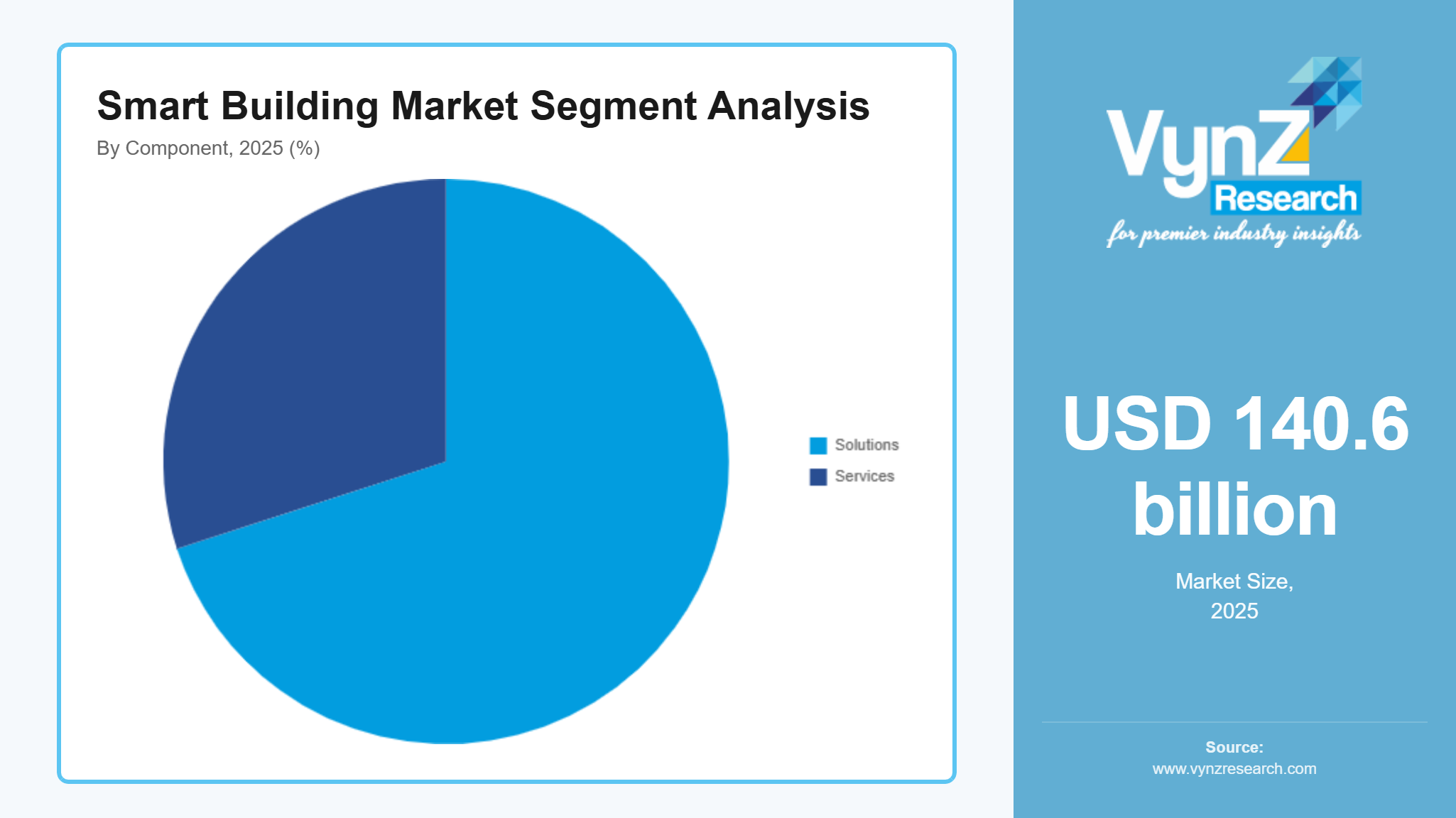
By Application
Commercial buildings represent the largest application category, with an estimated market share of 45% in 2025, due to their scale, energy intensity, and regulatory exposure. According to the Australian Government - Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water, the commercial building sector is responsible for around 25% of overall electricity use and 10% of total carbon emissions in Australia. This level of impact has positioned commercial real estate at the center of government-led efficiency and decarbonization efforts, accelerating adoption of smart energy management, automated HVAC, lighting controls, and building analytics. Large offices, retail centers, and mixed-use developments benefit most from intelligent systems that reduce operating costs while improving compliance and occupant experience. As a result, commercial properties continue to command the largest share of global smart building deployments.
Industrial buildings are the fastest-growing application category with a CAGR of 19.4% during the forecast period, as manufacturing facilities, warehouses, and processing plants increasingly adopt intelligent systems to improve energy efficiency, uptime, and operational safety. In Japan, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) promotes advanced energy management systems through its Top Runner Program, encouraging industries to deploy real-time monitoring, automation, and high-efficiency controls to meet ambitious performance benchmarks. These policy signals are accelerating the adoption of predictive maintenance, automated climate control, and energy tracking across large industrial campuses. Combined with broader digitalisation initiatives in manufacturing and logistics, smart building technologies are becoming integral to industrial operations, supporting cost reduction, regulatory compliance, and operational resilience. As a result, the industrial category is experiencing the fastest growth in smart building applications globally.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific is a rapidly growing market, fueled by rapid urbanization, large-scale construction, and government-led digital infrastructure programs. Countries such as China, Japan, Singapore, and Australia are embedding smart technologies into new commercial, residential, and industrial developments. In China, national development policies under the 14th Five-Year Plan emphasize energy efficiency, digital infrastructure, and smart city development, accelerating adoption of intelligent building controls and monitoring systems across urban centers. High population density, expanding industrial zones, and rising energy efficiency expectations are driving rapid deployment of smart building solutions. These dynamics position Asia Pacific as the region with the strongest growth momentum globally.
Europe
Europe represents a mature and regulation-driven smart building market, where adoption is shaped by stringent sustainability and energy performance requirements. Governments across the region continue to prioritize building efficiency, emissions reduction, and lifecycle performance, encouraging widespread use of automation, energy monitoring, and optimization technologies. While growth is steady rather than rapid, Europe remains a critical market for smart building retrofits, particularly across commercial and public infrastructure. The region’s emphasis on compliance, transparency, and long-term operational efficiency ensures consistent demand for advanced building solutions and services.
North America
North America held the largest market share of around 35% in 2025, driven by early technology adoption, large commercial real estate portfolios, and advanced digital infrastructure. Building owners across offices, healthcare facilities, universities, and public infrastructure have widely adopted automation, energy management, and analytics to improve operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. The region’s market leadership is reinforced by strong demand for retrofitting existing buildings with intelligent systems rather than relying solely on new construction. Mature cloud ecosystems, skilled facility management practices, and a strong focus on data-driven decision-making enable large-scale smart building deployments. As a result, North America continues to account for the highest installed base of smart building solutions worldwide.
Rest of the World
The rest of the world, including Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa, is seeing textile recycling evolve from informal, inefficient systems to more formalised, organised operations supported by policy changes and capital investment. Brazil and Mexico are developing pilot projects around recycling and waste-to-value initiatives to leverage textile consumption and automotive uses. Middle Eastern countries are establishing national circular programs and recycling facilities to reduce landfill waste and grow sustainable industry. In parts of Africa and South America, environmentally focused regulations and international partnerships are creating opportunities for formalised collection systems and cross-border recycling collaborations, which are expected to accelerate implementation in the near future.
The rest of the world, including Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa, represents an emerging growth opportunity for smart building technologies. Adoption is accelerating as governments modernize infrastructure, expand urban development, and place greater emphasis on energy efficiency and operational reliability. The Middle East is embedding smart building systems into large-scale urban and mixed-use developments, Latin America is strengthening energy efficiency frameworks for commercial construction, and African markets are increasingly deploying intelligent solutions to enhance building performance and resilience. Supported by greenfield construction, infrastructure investment, and sustainability-driven policies, these regions are building strong momentum. As smart technologies become integral to modern urban environments, the Rest of the World is expected to play an increasingly important role in shaping global smart building adoption over the coming decade.
Competitive Landscape / Company Insights
The smart building market is moderately fragmented, with a mix of global technology leaders, regional solution providers, and specialized service companies competing across different layers of the value chain. While large players offer comprehensive platforms covering automation, energy management, security, and analytics, smaller and mid-sized firms remain highly competitive by delivering customized solutions, vertical-specific expertise, and strong local execution.
Competition is increasingly centered on software intelligence, system interoperability, and long-term service capabilities rather than standalone hardware offerings. Vendors are differentiating through cloud-native platforms, AI-driven optimization, and integrated services that enable continuous building performance improvement. Strategic partnerships among technology vendors, system integrators, construction firms, and facility management providers are reshaping competitive positioning. As customers demand scalable, secure, and outcome-focused solutions, companies that combine technological depth with integration expertise and lifecycle support are strengthening their market presence in this evolving competitive environment.
Mini Profiles
Honeywell International Inc. delivers building automation and control solutions that enhance energy efficiency, safety, and operational performance across commercial and industrial facilities worldwide.
Johnson Controls International plc provides smart, healthy, and sustainable building solutions through integrated HVAC, building automation, security systems, and its OpenBlue digital platform.
Siemens AG enables intelligent and connected buildings by integrating automation systems, digital infrastructure, and energy management technologies to improve efficiency and sustainability.
Schneider Electric SE specializes in energy management and automation solutions that help buildings become more efficient, resilient, and digitally connected.
Cisco Systems, Inc. provides secure networking and digital infrastructure that support connected buildings, smart workplaces, and data-driven building operations.
Key Players
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric SE
- Johnson Controls International plc
- ABB Ltd.
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Hitachi, Ltd.
- IBM Corporation
- Intel Corporation
- Legrand SA
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Emerson Electric Co.
Recent Developments
November 2025 - ABB Ltd. unveiled ABB Ability TM BuildingPro, a cybersecure integration platform to connect, monitor, and optimize building operations across commercial real estate, education, healthcare, hospitality, and government portfolios. This solution aims to accelerate decarbonization and digital transformation in smart and sustainable buildings in 40+ countries.
November 2025 - Johnson Controls International plc announced the launch of Metasys 15.0, its flagship open building automation system designed for mission-critical environments. The system offers expanded scalability, multi-server resiliency, and integrated energy intelligence tools to help facility managers optimize performance, compliance, and decarbonization across large campuses or multi-site deployments.
September 2025 – At GSX 2025, Johnson Controls International plc showcased advanced integrated building safety systems that generate actionable intelligence, emphasizing data-driven resilience and enhanced security across building infrastructure.
September 2025 - Siemens AG signed a strategic partnership with Innovo Technology Services to deliver and integrate Siemens Building X smart building management solutions across the UAE.
Global Smart Building Market Coverage
Component Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- Solutions
- Services
Application Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
Global Smart Building Market by Region
- North America
- By Component
- By Application
- By Country - U.S., Canada, Mexico
- Europe
- By Component
- By Application
- By Country - Germany, U.K., France, Italy, Spain, Russia, Rest of Europe
- Asia-Pacific (APAC)
- By Component
- By Application
- By Country - China, Japan, India, South Korea, Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia, Rest of Asia-Pacific
- Rest of the World (RoW)
- By Component
- By Application
- By Country - Brazil, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, U.A.E., Other Countries
Table of Contents for Smart Building Market Report
1. Research Overview
1.1. The Report Offers
1.2. Market Coverage
1.2.1. By
Component
1.2.2. By
Application
1.3. Research Phases
1.4. Limitations
1.5. Market Methodology
1.5.1. Data Sources
1.5.1.1.
Primary Research
1.5.1.2.
Secondary Research
1.5.2. Methodology
1.5.2.1.
Data Exploration
1.5.2.2.
Forecast Parameters
1.5.2.3.
Data Validation
1.5.2.4.
Assumptions
1.5.3. Study Period & Data Reporting Unit
2. Executive Summary
3. Industry Overview
3.1. Industry Dynamics
3.1.1. Market Growth Drivers
3.1.2. Market Restraints
3.1.3. Key Market Trends
3.1.4. Major Opportunities
3.2. Industry Ecosystem
3.2.1. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
3.2.2. Recent Development Analysis
3.2.3. Value Chain Analysis
3.3. Competitive Insight
3.3.1. Competitive Position of Industry
Players
3.3.2. Market Attractive Analysis
3.3.3. Market Share Analysis
4. Global Market Estimate and Forecast
4.1. Global Market Overview
4.2. Global Market Estimate and Forecast to 2035
5. Market Segmentation Estimate and Forecast
5.1. By Component
5.1.1. Solutions
5.1.1.1. Market Definition
5.1.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.1.2. Services
5.1.2.1. Market Definition
5.1.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.2. By Application
5.2.1. Residential
5.2.1.1. Market Definition
5.2.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.2.2. Commercial
5.2.2.1. Market Definition
5.2.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.2.3. Industrial
5.2.3.1. Market Definition
5.2.3.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
6. North America Market Estimate and Forecast
6.1. By
Component
6.2. By
Application
6.2.1.
U.S. Market Estimate and Forecast
6.2.2.
Canada Market Estimate and Forecast
6.2.3.
Mexico Market Estimate and Forecast
7. Europe Market Estimate and Forecast
7.1. By
Component
7.2. By
Application
7.2.1.
Germany Market Estimate and Forecast
7.2.2.
U.K. Market Estimate and Forecast
7.2.3.
France Market Estimate and Forecast
7.2.4.
Italy Market Estimate and Forecast
7.2.5.
Spain Market Estimate and Forecast
7.2.6.
Russia Market Estimate and Forecast
7.2.7.
Rest of Europe Market Estimate and Forecast
8. Asia-Pacific (APAC) Market Estimate and Forecast
8.1. By
Component
8.2. By
Application
8.2.1.
China Market Estimate and Forecast
8.2.2.
Japan Market Estimate and Forecast
8.2.3.
India Market Estimate and Forecast
8.2.4.
South Korea Market Estimate and Forecast
8.2.5.
Vietnam Market Estimate and Forecast
8.2.6.
Thailand Market Estimate and Forecast
8.2.7.
Malaysia Market Estimate and Forecast
8.2.8.
Rest of Asia-Pacific Market Estimate and Forecast
9. Rest of the World (RoW) Market Estimate and Forecast
9.1. By
Component
9.2. By
Application
9.2.1.
Brazil Market Estimate and Forecast
9.2.2.
Saudi Arabia Market Estimate and Forecast
9.2.3.
South Africa Market Estimate and Forecast
9.2.4.
U.A.E. Market Estimate and Forecast
9.2.5.
Other Countries Market Estimate and Forecast
10. Company Profiles
10.1.
Honeywell International Inc.
10.1.1.
Snapshot
10.1.2.
Overview
10.1.3.
Offerings
10.1.4.
Financial
Insight
10.1.5.
Recent
Developments
10.2.
Siemens AG
10.2.1.
Snapshot
10.2.2.
Overview
10.2.3.
Offerings
10.2.4.
Financial
Insight
10.2.5.
Recent
Developments
10.3.
Schneider Electric SE
10.3.1.
Snapshot
10.3.2.
Overview
10.3.3.
Offerings
10.3.4.
Financial
Insight
10.3.5.
Recent
Developments
10.4.
Johnson Controls International plc
10.4.1.
Snapshot
10.4.2.
Overview
10.4.3.
Offerings
10.4.4.
Financial
Insight
10.4.5.
Recent
Developments
10.5.
ABB Ltd.
10.5.1.
Snapshot
10.5.2.
Overview
10.5.3.
Offerings
10.5.4.
Financial
Insight
10.5.5.
Recent
Developments
10.6.
Cisco Systems, Inc.
10.6.1.
Snapshot
10.6.2.
Overview
10.6.3.
Offerings
10.6.4.
Financial
Insight
10.6.5.
Recent
Developments
10.7.
Hitachi, Ltd.
10.7.1.
Snapshot
10.7.2.
Overview
10.7.3.
Offerings
10.7.4.
Financial
Insight
10.7.5.
Recent
Developments
10.8.
IBM Corporation
10.8.1.
Snapshot
10.8.2.
Overview
10.8.3.
Offerings
10.8.4.
Financial
Insight
10.8.5.
Recent
Developments
10.9.
Intel Corporation
10.9.1.
Snapshot
10.9.2.
Overview
10.9.3.
Offerings
10.9.4.
Financial
Insight
10.9.5.
Recent
Developments
10.10.
Legrand SA
10.10.1.
Snapshot
10.10.2.
Overview
10.10.3.
Offerings
10.10.4.
Financial
Insight
10.10.5.
Recent
Developments
10.11.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
10.11.1.
Snapshot
10.11.2.
Overview
10.11.3.
Offerings
10.11.4.
Financial
Insight
10.11.5.
Recent
Developments
10.12.
Emerson Electric Co.
10.12.1.
Snapshot
10.12.2.
Overview
10.12.3.
Offerings
10.12.4.
Financial
Insight
10.12.5.
Recent
Developments
11. Appendix
11.1. Exchange Rates
11.2. Abbreviations
Note: Financial insight and recent developments of different companies are subject to the availability of information in the secondary domain.
Purchase Options
Latest Report
Research Methodology
- Desk Research / Pilot Interviews
- Build Market Size Model
- Research and Analysis
- Final Deliverable
Connect With Our Sales Team
- Toll-Free: +1-888-253-3960
- Phone: +91 9960 288 381
- Email: enquiry@vynzresearch.com
Smart Building Market
