Digital Substation Market Size & Share | Growth Forecast Report (2026-2035)
Industry Insight by Component (Hardware, Software, Services), by Installation Type (New Installations, Retrofit / Upgrade Projects), by Voltage Level (Low Voltage, Medium Voltage, High Voltage), by Substation Type (Transmission Substations, Distribution Substations), by End User (Utilities, Industrial / Commercial)
| Status : Published | Published On : Feb, 2026 | Report Code : VRSME9181 | Industry : Semiconductor & Electronics | Available Format :

|
Page : 140 |
Digital Substation Market Size & Share | Growth Forecast Report (2026-2035)
Industry Insight by Component (Hardware, Software, Services), by Installation Type (New Installations, Retrofit / Upgrade Projects), by Voltage Level (Low Voltage, Medium Voltage, High Voltage), by Substation Type (Transmission Substations, Distribution Substations), by End User (Utilities, Industrial / Commercial)
Digital Substation Market Overview
The global digital substation market which was valued at approximately USD 10.40 billion in 2025 and is estimated to reach around USD 11.05 billion in 2026, is projected to reach around USD 19.10 billion by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of about 6.2% during the forecast period from 2026 to 2035.
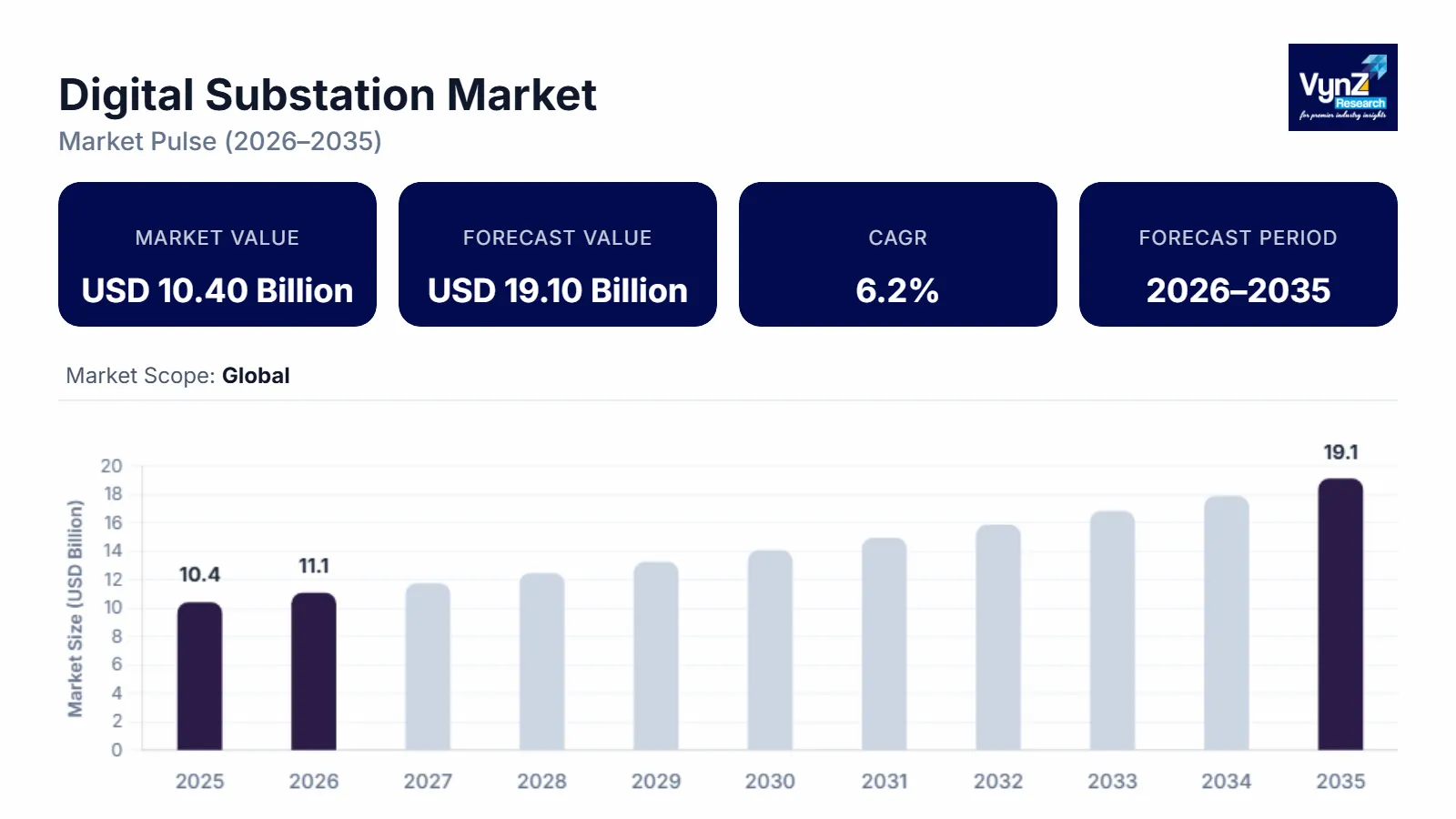
Market expansion is primarily supported by ongoing grid modernization initiatives and the accelerating replacement of conventional substations with digitally enabled architectures across developed and emerging power systems.
Adoption is supported by utilities’ emphasis on operational reliability, grid visibility, and lifecycle cost optimization, aligned with formal grid modernization frameworks such as initiatives led by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Electricity. These programs promote advanced monitoring, automated protection, and standardized communication architectures across transmission and distribution networks. Digital substations enable real-time system visibility, faster fault isolation, and condition-based maintenance through intelligent electronic devices and interoperable communication protocols. Public investment programs focused on smart grids and cybersecurity-aligned infrastructure across North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific continue to sustain demand from utility and large industrial end users.
Digital Substation Market Dynamics
Market Trends
The digital substation market is undergoing a structural shift toward communication-centric and software-defined power infrastructure, aligned with grid modernization programs promoted by public energy authorities and transmission system operators. Frameworks supported by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Electricity and European transmission bodies under ENTSO-E emphasize digital protection, standardized communication, and reduced physical wiring to improve grid reliability and operational efficiency. This has accelerated the transition from copper-intensive architectures to IEC 61850-based process bus systems, supporting interoperability and faster deployment.
Utilities are increasing deployment of merging units, digital sensors, and intelligent protection relays to improve real-time visibility and fault response, consistent with national grid modernization roadmaps in regions such as the United States, Europe, and India. Government-backed renewable integration targets and grid codes issued by authorities such as the Central Electricity Authority (India) and European regulators are reinforcing demand for substations capable of managing bidirectional power flows and variable generation profiles while maintaining system stability.
Growth Drivers
Globally, utilities are transitioning from legacy electromechanical systems toward digital, communication-based substation architectures. The adoption of IEC 61850 standards enables continuous data exchange, flexible system engineering, and automated protection schemes while improving interoperability and operational reliability. These capabilities significantly reduce wiring complexity and enhance system scalability, making digital substations a foundational element of modern transmission and distribution networks.
The accelerated deployment of renewable and distributed energy resources is another primary growth driver. Increasing integration of wind, solar, and decentralized generation assets requires substations capable of managing load variability, bidirectional power flow, and dynamic grid conditions. Digital substations support automated voltage and frequency regulation, real-time system monitoring, and rapid protection response, contributing to improved grid resilience and stability.
In addition, digital substations incorporate intelligent electronic devices, sensors, and advanced relays that support continuous condition monitoring and early fault detection. This enables utilities to reduce outage durations, implement predictive maintenance strategies, and optimize asset performance over the operational lifecycle. Remote diagnostics and centralized control further contribute to lower operating expenditures and improved long-term system efficiency.
Market Restraints / Challenges
The shift from conventional to digital substation architectures requires significant capital outlay for SCADA systems, fiber-optic communication networks, intelligent electronic devices, and supporting software platforms. Government reports, such as the U.S. Department of Energy’s Grid Modernization Multi-Year Program Plan and India’s Central Electricity Authority Transmission Report 2025, highlight that utilities in developing and emerging economies face budget constraints and limited skilled personnel, which can slow adoption.
Digital substations also necessitate advanced cybersecurity frameworks to ensure secure communication, device authentication, and continuous intrusion monitoring. National standards, including the U.S. NERC CIP (Critical Infrastructure Protection) and Europe’s NIS2 Directive, mandate secure protocols, redundancy mechanisms, and compliance-driven architectures, adding to project complexity and lifecycle costs. As substations become increasingly interconnected, exposure to cyber threats and operational vulnerabilities remains a significant challenge, requiring ongoing investment in monitoring, system upgrades, and risk mitigation strategies.
Market Opportunities
The transition from conventional to digital substation architectures demands substantial capital investment in SCADA systems, fiber-optic networks, intelligent electronic devices, and supporting software. Reports such as the U.S. DOE Grid Modernization Multi-Year Program Plan and India’s Central Electricity Authority Transmission Report 2025 note that limited budgets and skilled personnel in developing and emerging economies can constrain adoption.
Digital substations require robust cybersecurity frameworks to ensure secure communication, device authentication, and continuous intrusion monitoring. Compliance with standards like U.S. NERC CIP and Europe’s NIS2 Directive introduces additional complexity and lifecycle costs. As substations become increasingly interconnected, exposure to cyber threats and operational vulnerabilities persists, necessitating continuous investment in monitoring, system upgrades, and risk mitigation.
Global Digital Substation Market Report Coverage
|
Report Metric |
Details |
|
Historical Period |
2020 - 2024 |
|
Base Year Considered |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026 - 2035 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 10.40 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast in 2035 |
USD 19.10 Billion |
|
Growth Rate |
6.2% |
|
Segments Covered in the Report |
By Component, By Installation Type, By Voltage Level, By Substation Type, By End User |
|
Report Scope |
Market Trends, Drivers, and Restraints; Revenue Estimation and Forecast; Segmentation Analysis; Companies’ Strategic Developments; Market Share Analysis of Key Players; Company Profiling |
|
Regions Covered in the Report |
North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, Other Regions |
|
Key Companies |
ABB Ltd, Cisco Systems Inc, Eaton Corporation plc, Emerson Electric Co., General Electric Company, Hitachi Energy Ltd., Honeywell International Inc, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Rockwell Automation, Schneider Electric, Siemens AG, Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions, Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Larsen & Toubro Ltd, Omicron Electronics, Alstom Grid |
|
Customization |
Available upon request |
Digital Substation Market Segmentation
By Component
Hardware is projected to account for approximately 51% of total market revenue in 2025. This reflects the critical role of intelligent electronic devices (IEDs), digital relays, communication modules, and control systems in digital substations, which form the backbone of operational reliability and automated protection.
Software solutions, including analytics platforms, automation tools, and monitoring systems, are estimated at around 23%, driven by utilities’ emphasis on real-time operational intelligence, predictive maintenance, and centralized diagnostics.
Services including installation, integration, consulting, and lifecycle support contribute approximately 22%, supporting digital adoption across new and upgraded substations while enhancing long-term operational efficiency and minimizing downtime.
By Installation Type
New installations are anticipated to represent roughly 56% of market revenue in 2025, supported by greenfield digital substations designed with fully integrated communication and automation architectures.
Retrofit or upgrade projects account for approximately 44%, reflecting modernization of legacy substations with fiber-optic networks, IEDs, and advanced protection relays. Utilities pursue retrofits to extend asset lifecycles, enhance reliability, and incrementally improve system performance while managing capital expenditures.
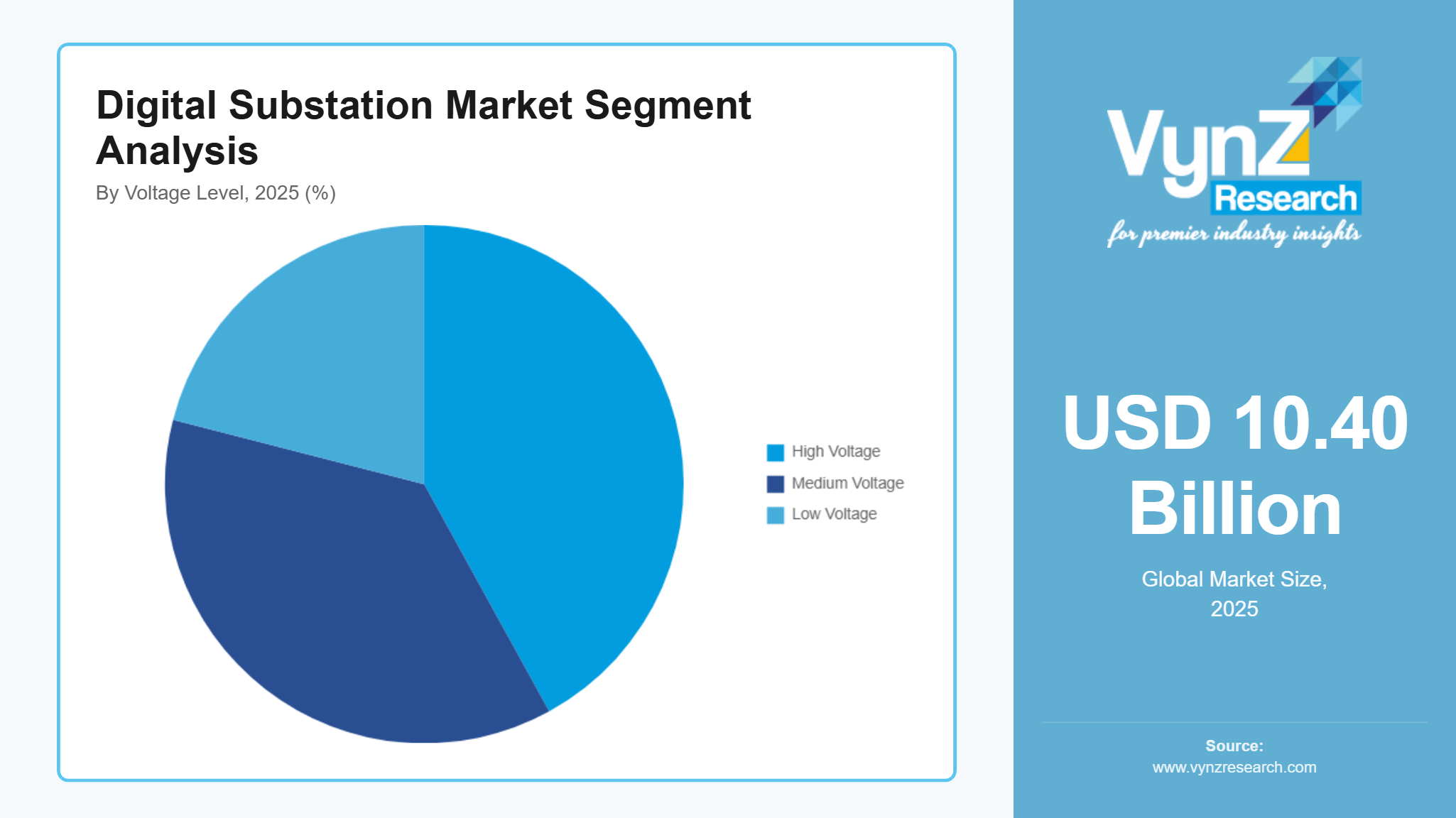
By Voltage Level
Medium voltage substations are expected to hold around 42% of total revenue in 2025, supported by regional distribution networks, industrial microgrids, and localized energy management applications.
High voltage substations represent approximately 37%, driven by transmission network modernization and adoption of automated monitoring and protection systems that enable improved grid resilience and fault management.
Low voltage substations contribute roughly 21%, primarily in compact distribution and industrial facilities where automation, monitoring, and local load control are critical.
By Substation Type
Distribution substations are estimated at approximately 57% of revenue in 2025, reflecting widespread network upgrades and integration of distributed energy resources.
Transmission substations account for around 43%, driven by the need for high-precision control, advanced protection, and automation to maintain stability in bulk power transfer across transmission corridors.
By End User
Utilities are projected to contribute approximately 63% of total market revenue in 2025. This is underpinned by ongoing investments in grid modernization, renewable integration, regulatory compliance, and centralized monitoring systems.
Industrial and commercial end users including manufacturing facilities, airports, railways, and critical infrastructure represent roughly 37%, supported by demand for reliable power supply, integration with automation solutions, and quality assurance requirements.
Regional Insights
North America
North America is estimated to hold approximately 31% of the global market in 2025. Utilities are modernizing aging transmission and distribution networks to improve resilience, integrate digital monitoring, and implement automated protection. Federal initiatives, including the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Grid Modernization Multi-Year Program Plan and Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) modernization programs, support SCADA upgrades, cybersecurity frameworks, and predictive maintenance solutions. Utilities are deploying fiber-optic networks, merging units, and phasor measurement units (PMUs) to optimize operational efficiency. Rising renewable energy penetration in states such as Texas, California, and New York further reinforces market adoption. Key vendors include ABB, Siemens Energy, SEL, and GE Grid Solutions.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific is projected to account for roughly 35% of the market in 2025. Rapid urbanization, growing electricity demand, and government-led grid modernization programs drive adoption. China leads with large-scale ultra-high-voltage (UHV) transmission projects and renewable energy integration, deploying IEC 61850-compliant digital substations via utilities such as SGCC and CSG. In India, programs such as the Resilient and Digital Substation Scheme (RDSS) and national smart grid initiatives are accelerating adoption, with utilities like PGCIL, NTPC, and state DISCOMs deploying digital relays, merging units, and fiber networks. Growth is fueled by high-volume substation construction, integration of renewables, and an emphasis on grid stability.
Europe
Europe represents approximately 18% of the market in 2025. Adoption is driven by decarbonization policies and modernization of aging infrastructure. Germany, the UK, France, Spain, and the Netherlands are investing in SCADA upgrades, IEC 61850 relays, and process bus systems. Offshore wind projects and cross-border grid interconnections necessitate advanced automation, high-voltage control, and predictive maintenance. Cybersecurity regulations, such as the NIS2 Directive, require encrypted communication, intrusion detection, and secure data exchange. Key vendors include ABB, Siemens Energy, Schneider Electric, and Toshiba
Other Regions
The remaining regions collectively contribute approximately 16% of the global market. Growth is supported by infrastructure modernization, renewable energy integration, and government programs for resilient power networks. Although adoption is slower compared with North America, Asia Pacific, and Europe, these regions represent strategic long-term opportunities for digital substation deployment.
Competitive Landscape / Company Insights
The market is moderately competitive, with global and regional players focusing on technology innovation, cost efficiency, and geographic expansion. Key vendors including ABB, Siemens Energy, Schneider Electric, and GE Grid Solutions offer IEC 61850-compliant systems, predictive maintenance platforms, and cybersecurity solutions. Adoption is supported by government programs such as the U.S. DOE Grid Modernization Plan, FERC initiatives, and Europe’s NIS2 Directive, which drive deployment of secure, automated, and resilient substations. These regulatory frameworks encourage vendors to strengthen their market position and secure long-term utility and industrial contracts across North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific.
Mini Profiles
ABB provides IEC 61850-compliant digital substations, automation, and protection solutions, supported by a strong global network, predictive maintenance, and cybersecurity capabilities, enabling utilities to modernize transmission and distribution grids efficiently.
Siemens delivers premium digital substation systems, including process bus architectures and renewable integration, leveraging advanced R&D, automation, and service networks to ensure high reliability and operational efficiency globally.
General Electric offers digital substations, advanced protection relays, and SCADA integration, supported by strategic partnerships and local manufacturing, focusing on predictive maintenance, asset management, and renewable energy integration.
Schneider Electric specializes in smart grid and digital substation solutions, emphasizing energy efficiency, automation, remote monitoring, and IEC 61850 compliance, backed by global digital capabilities and secure grid infrastructure support.
Cisco supports digital substations with rugged industrial networking, IEC 61850 communication, cybersecurity, edge computing, and resilient automation infrastructure, enabling secure, real-time data exchange and grid modernization across utility operations worldwide.
Key Players
- ABB Ltd.
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- Eaton Corporation plc
- Emerson Electric Co.
- General Electric Company
- Hitachi Energy Ltd.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Rockwell Automation, Inc.
- Schneider Electric
- Siemens AG
- Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions
- Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories
- Larsen & Toubro Ltd.
- Omicron Electronics
- Alstom Grid
Recent Developments
January 2026 - ABB has secured a major order from Titagarh Rail Systems Ltd. which shall supply advanced propulsion systems and Train Control and Management System (TCMS) software for the Mumbai Metro Lines. These upcoming metro lines are key to Mumbai’s rail network in significantly improving connectivity between key geographical locations, ease road traffic and reduce travel time for daily commuters.
January 2026 - Cisco recently launched its revamped 360 Partner Program, designed to support channel partners with AI‑ready tools and resources across security, networking, cloud, and infrastructure portfolios, aligning its ecosystem with AI and digital transformation demand.
November 2025 - Rockwell Automation announced plans to build a 1 million‑square‑foot greenfield manufacturing facility in Wisconsin as part of a multi-year investment to expand advanced production capacity and strengthen U.S. manufacturing capabilities.
Global Digital Substation Market Coverage
Component Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
Installation Type Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- New Installations
- Retrofit / Upgrade Projects
Voltage Level Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- Low Voltage
- Medium Voltage
- High Voltage
Substation Type Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- Transmission Substations
- Distribution Substations
End User Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- Utilities
- Industrial / Commercial
Global Digital Substation Market by Region
- North America
- By Component
- By Installation Type
- By Voltage Level
- By Substation Type
- By End User
- By Country - U.S., Canada, Mexico
- Europe
- By Component
- By Installation Type
- By Voltage Level
- By Substation Type
- By End User
- By Country - Germany, U.K., France, Italy, Spain, Russia, Rest of Europe
- Asia-Pacific (APAC)
- By Component
- By Installation Type
- By Voltage Level
- By Substation Type
- By End User
- By Country - China, Japan, India, South Korea, Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia, Rest of Asia-Pacific
- Rest of the World (RoW)
- By Component
- By Installation Type
- By Voltage Level
- By Substation Type
- By End User
- By Country - Brazil, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, U.A.E., Other Countries
Table of Contents for Digital Substation Market Report
1. Research Overview
1.1. The Report Offers
1.2. Market Coverage
1.2.1. By
Component
1.2.2. By
Installation Type
1.2.3. By
Voltage Level
1.2.4. By
Substation Type
1.2.5. By
End User
1.3. Research Phases
1.4. Limitations
1.5. Market Methodology
1.5.1. Data Sources
1.5.1.1.
Primary Research
1.5.1.2.
Secondary Research
1.5.2. Methodology
1.5.2.1.
Data Exploration
1.5.2.2.
Forecast Parameters
1.5.2.3.
Data Validation
1.5.2.4.
Assumptions
1.5.3. Study Period & Data Reporting Unit
2. Executive Summary
3. Industry Overview
3.1. Industry Dynamics
3.1.1. Market Growth Drivers
3.1.2. Market Restraints
3.1.3. Key Market Trends
3.1.4. Major Opportunities
3.2. Industry Ecosystem
3.2.1. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
3.2.2. Recent Development Analysis
3.2.3. Value Chain Analysis
3.3. Competitive Insight
3.3.1. Competitive Position of Industry
Players
3.3.2. Market Attractive Analysis
3.3.3. Market Share Analysis
4. Global Market Estimate and Forecast
4.1. Global Market Overview
4.2. Global Market Estimate and Forecast to 2035
5. Market Segmentation Estimate and Forecast
5.1. By Component
5.1.1. Hardware
5.1.1.1. Market Definition
5.1.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.1.2. Software
5.1.2.1. Market Definition
5.1.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.1.3. Services
5.1.3.1. Market Definition
5.1.3.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.2. By Installation Type
5.2.1. New Installations
5.2.1.1. Market Definition
5.2.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.2.2. Retrofit / Upgrade Projects
5.2.2.1. Market Definition
5.2.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.3. By Voltage Level
5.3.1. Low Voltage
5.3.1.1. Market Definition
5.3.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.3.2. Medium Voltage
5.3.2.1. Market Definition
5.3.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.3.3. High Voltage
5.3.3.1. Market Definition
5.3.3.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.4. By Substation Type
5.4.1. Transmission Substations
5.4.1.1. Market Definition
5.4.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.4.2. Distribution Substations
5.4.2.1. Market Definition
5.4.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.5. By End User
5.5.1. Utilities
5.5.1.1. Market Definition
5.5.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.5.2. Industrial / Commercial
5.5.2.1. Market Definition
5.5.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
6. North America Market Estimate and Forecast
6.1. By
Component
6.2. By
Installation Type
6.3. By
Voltage Level
6.4. By
Substation Type
6.5. By
End User
6.5.1.
U.S. Market Estimate and Forecast
6.5.2.
Canada Market Estimate and Forecast
6.5.3.
Mexico Market Estimate and Forecast
7. Europe Market Estimate and Forecast
7.1. By
Component
7.2. By
Installation Type
7.3. By
Voltage Level
7.4. By
Substation Type
7.5. By
End User
7.5.1.
Germany Market Estimate and Forecast
7.5.2.
U.K. Market Estimate and Forecast
7.5.3.
France Market Estimate and Forecast
7.5.4.
Italy Market Estimate and Forecast
7.5.5.
Spain Market Estimate and Forecast
7.5.6.
Russia Market Estimate and Forecast
7.5.7.
Rest of Europe Market Estimate and Forecast
8. Asia-Pacific (APAC) Market Estimate and Forecast
8.1. By
Component
8.2. By
Installation Type
8.3. By
Voltage Level
8.4. By
Substation Type
8.5. By
End User
8.5.1.
China Market Estimate and Forecast
8.5.2.
Japan Market Estimate and Forecast
8.5.3.
India Market Estimate and Forecast
8.5.4.
South Korea Market Estimate and Forecast
8.5.5.
Vietnam Market Estimate and Forecast
8.5.6.
Thailand Market Estimate and Forecast
8.5.7.
Malaysia Market Estimate and Forecast
8.5.8.
Rest of Asia-Pacific Market Estimate and Forecast
9. Rest of the World (RoW) Market Estimate and Forecast
9.1. By
Component
9.2. By
Installation Type
9.3. By
Voltage Level
9.4. By
Substation Type
9.5. By
End User
9.5.1.
Brazil Market Estimate and Forecast
9.5.2.
Saudi Arabia Market Estimate and Forecast
9.5.3.
South Africa Market Estimate and Forecast
9.5.4.
U.A.E. Market Estimate and Forecast
9.5.5.
Other Countries Market Estimate and Forecast
10. Company Profiles
10.1. ABB Ltd.
10.1.1.
Snapshot
10.1.2.
Overview
10.1.3.
Offerings
10.1.4.
Financial
Insight
10.1.5. Recent
Developments
10.2. Cisco Systems Inc.
10.2.1.
Snapshot
10.2.2.
Overview
10.2.3.
Offerings
10.2.4.
Financial
Insight
10.2.5. Recent
Developments
10.3. Eaton Corporation plc
10.3.1.
Snapshot
10.3.2.
Overview
10.3.3.
Offerings
10.3.4.
Financial
Insight
10.3.5. Recent
Developments
10.4. Emerson Electric Co.
10.4.1.
Snapshot
10.4.2.
Overview
10.4.3.
Offerings
10.4.4.
Financial
Insight
10.4.5. Recent
Developments
10.5. General Electric Company
10.5.1.
Snapshot
10.5.2.
Overview
10.5.3.
Offerings
10.5.4.
Financial
Insight
10.5.5. Recent
Developments
10.6. Hitachi Energy Ltd.
10.6.1.
Snapshot
10.6.2.
Overview
10.6.3.
Offerings
10.6.4.
Financial
Insight
10.6.5. Recent
Developments
10.7. Honeywell International Inc.
10.7.1.
Snapshot
10.7.2.
Overview
10.7.3.
Offerings
10.7.4.
Financial
Insight
10.7.5. Recent
Developments
10.8. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
10.8.1.
Snapshot
10.8.2.
Overview
10.8.3.
Offerings
10.8.4.
Financial
Insight
10.8.5. Recent
Developments
10.9. Rockwell Automation, Inc.
10.9.1.
Snapshot
10.9.2.
Overview
10.9.3.
Offerings
10.9.4.
Financial
Insight
10.9.5. Recent
Developments
10.10. Schneider Electric
10.10.1.
Snapshot
10.10.2.
Overview
10.10.3.
Offerings
10.10.4.
Financial
Insight
10.10.5. Recent
Developments
10.11. Siemens AG
10.11.1.
Snapshot
10.11.2.
Overview
10.11.3.
Offerings
10.11.4.
Financial
Insight
10.11.5. Recent
Developments
10.12. Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions
10.12.1.
Snapshot
10.12.2.
Overview
10.12.3.
Offerings
10.12.4.
Financial
Insight
10.12.5. Recent
Developments
10.13. Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories
10.13.1.
Snapshot
10.13.2.
Overview
10.13.3.
Offerings
10.13.4.
Financial
Insight
10.13.5. Recent
Developments
10.14. Larsen & Toubro Ltd.
10.14.1.
Snapshot
10.14.2.
Overview
10.14.3.
Offerings
10.14.4.
Financial
Insight
10.14.5. Recent
Developments
10.15. Omicron Electronics
10.15.1.
Snapshot
10.15.2.
Overview
10.15.3.
Offerings
10.15.4.
Financial
Insight
10.15.5. Recent
Developments
10.16. Alstom Grid
10.16.1.
Snapshot
10.16.2.
Overview
10.16.3.
Offerings
10.16.4.
Financial
Insight
10.16.5. Recent
Developments
11. Appendix
11.1. Exchange Rates
11.2. Abbreviations
Note: Financial insight and recent developments of different companies are subject to the availability of information in the secondary domain.
Frequently Asked Questions
Purchase Options
Latest Report
Research Methodology
- Desk Research / Pilot Interviews
- Build Market Size Model
- Research and Analysis
- Final Deliverable
Connect With Our Sales Team
- Toll-Free: +1-888-253-3960
- Phone: +91 9960 288 381
- Email: enquiry@vynzresearch.com
Digital Substation Market
