Middle East Energy Efficient Buildings Market Size & Share - Growth Forecast Report (2026-2035)
Industry Insight by Building Type (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Institutional), by Technology (Energy Management Systems, HVAC Controls & Equipment, Lighting & Fixtures, Building Envelope & Insulation Materials, Renewable Energy Integration), by Application (New Construction, Renovation & Retrofitting, Maintenance & Upgrades), by End User (Residential Property Developers, Commercial & Office Infrastructure, Institutional & Government Projects, Industrial Facilities), by Material (Glass Wool & Mineral Wool, Expanded & Extruded Polystyrene, Polyurethane, Others)
| Status : Published | Published On : Feb, 2026 | Report Code : VREP3053 | Industry : Energy & Power | Available Format :

|
Page : 146 |
Middle East Energy Efficient Buildings Market Size & Share - Growth Forecast Report (2026-2035)
Industry Insight by Building Type (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Institutional), by Technology (Energy Management Systems, HVAC Controls & Equipment, Lighting & Fixtures, Building Envelope & Insulation Materials, Renewable Energy Integration), by Application (New Construction, Renovation & Retrofitting, Maintenance & Upgrades), by End User (Residential Property Developers, Commercial & Office Infrastructure, Institutional & Government Projects, Industrial Facilities), by Material (Glass Wool & Mineral Wool, Expanded & Extruded Polystyrene, Polyurethane, Others)
Middle East Energy Efficient Buildings Market Overview
The middle east energy efficient buildings market, which was valued at approximately USD 715.4 million in 2025 and is estimated to reach around USD 868.5 million in 2026, is projected to reach close to 3,203.9 by 2035, expanding at a CAGR of about 15.6% during the forecast period from 2026 to 2035.
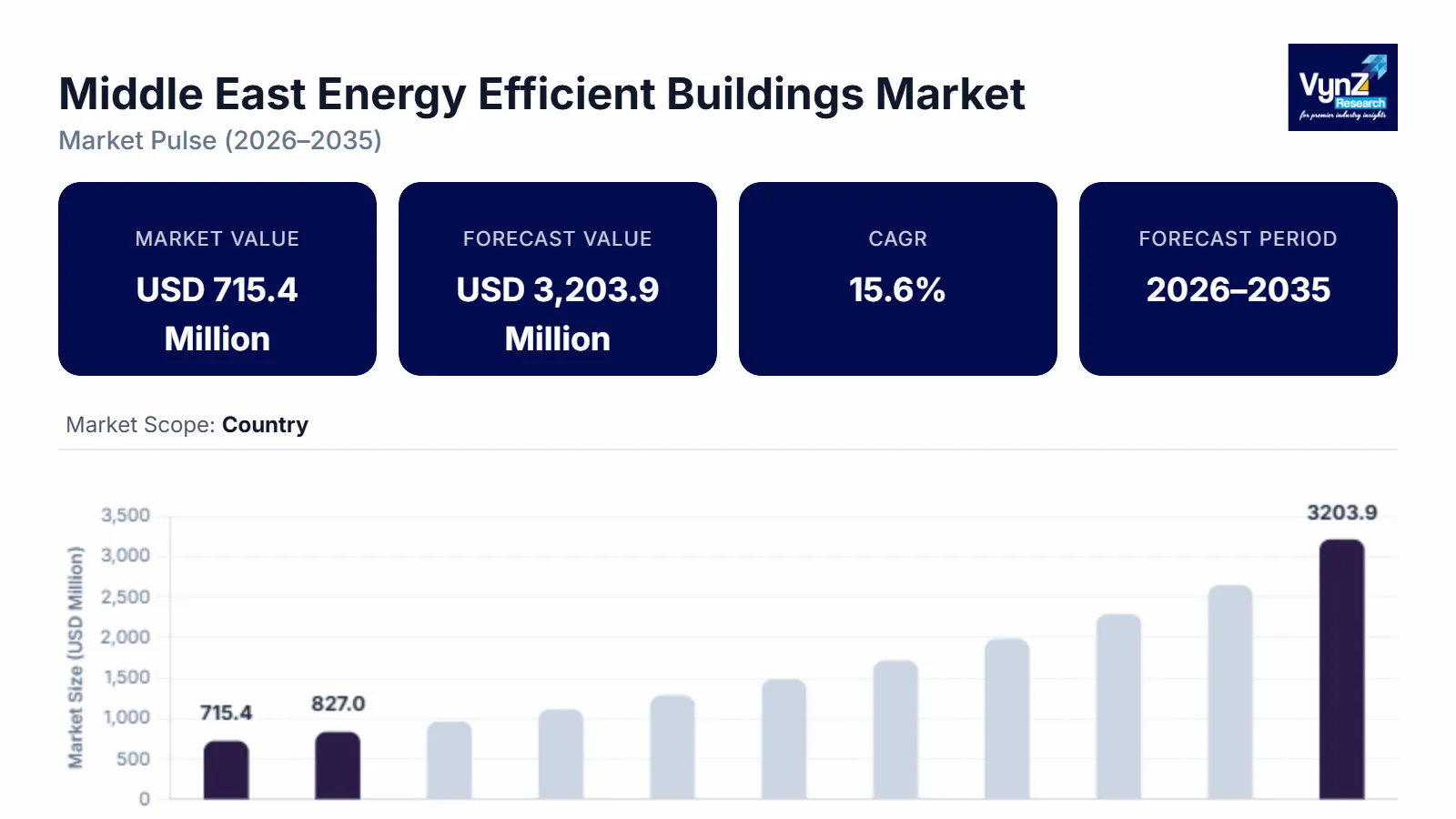
The market is expanding because governments across the Middle East are increasingly integrating energy performance standards into building regulations, embedding sustainability goals within national visions and urban development strategies. The increased energy use resulting from both extreme climate conditions and rapid urbanisation, combined with a need for reduced operational costs and enhanced energy security, has resulted in the widespread adoption of energy management systems, high-performance insulation, and smart building technologies. Green building certifications and public-private partnerships, along with incentives for sustainable construction practices, are motivating builders to utilise new and innovative materials and automated control systems. Therefore, these various factors are creating a momentum that will continue to increase the number of energy-efficient buildings, and therefore create a demand for efficiency solutions for all construction and retrofitting projects, as well as modernising existing infrastructure, as According to the International Energy Agency, energy efficiency investment across the Middle East increased by about 40% in 2024, reflecting accelerating regional infrastructure modernization.
Middle East Energy Efficient Buildings Market Dynamics
Market Trends
The construction sector is moving toward increased use of combined advanced building technologies and regulatory compliance frameworks to increase the overall energy efficiency and sustainability of all new and existing buildings. The increased adoption of green building standards and stricter energy codes by developers and policymakers has driven advancements in high-performance building envelopes and intelligent energy management systems, as well as climate-responsive designs, which have reduced operational inefficiencies for a wide range of building types. These efforts are being furthered through the advancement of "smart cities" and the increasing focus on thermal optimisation in regions with extreme heat conditions, and the increased adoption of high-performance materials, automated control methods, and integrated whole-building energy monitoring and analytics that will meet the national sustainability objectives and urban growth plans, with global rooftop solar PV capacity increasing by 22% in 2024, reinforcing integration of distributed building-level energy technologies.
Growth Drivers
The main driver of a growing energy management market has been governmental policies that promote energy efficiency and sustainable development of the built environment. National and regional governments have developed increasingly strict building codes, performance standards, and incentives for the use of energy-efficient design, materials, and systems. The regulatory framework established by national and regional authorities to support these energy security objectives includes reducing dependence on traditional energy supplies and mitigating peak loads on the grid. As the focus among stakeholders has increased with respect to reducing lifecycle costs and improving environmental performance, there has also been an increase in the adoption of energy-conscious practices by developers, investors, and facility managers, which has generated consistent demand for energy management technologies across all segments, including commercial, residential, and institutional, as According to the International Energy Agency, global investment in energy efficiency reached USD 660 billion in 2024 driven by strong policy support.
Market Restraints / Challenges
The Middle Eastern market is impacted by many factors (structural and implementation) that slow down its overall development in terms of energy efficiency. For many, the high initial capital required to implement "energy-efficient" products and technologies remains a major barrier to entry and use; while long-term operational cost savings exist, this does not offset the up-front cost barrier to entry. There are also barriers created by a lack of knowledge and/or awareness of the energy-saving benefits of advanced energy efficiency practices amongst all stakeholder groups, including architects, building owners, project financiers, and end-users, which results in slower integration of these practices into the built environment. A third barrier to entry and growth exists as a result of inconsistent regulatory requirements and varying levels of code enforcement in each country, resulting in uncertainty and complexity when it comes to planning and compliance with energy efficiency regulations. Lastly, there are skill gaps and technical limitations at various stages (design, construction, and retrofit) that limit the ability to develop and deliver buildings that meet energy efficiency standards, and therefore limit the rate at which new or existing buildings can be developed or improved in terms of their energy performance.
Market Opportunities
The market is likely to experience a lot of growth due to an increase in the number of organisations making sustainability commitments, as well as advancements in technology that enable more efficient use of energy and funding mechanisms that incentivise energy-efficient development and retrofitting. In addition, expansion of green financing options (public-private partnerships) will provide more accessibility to funds for energy efficiency improvements for large commercial and institutional sectors. There is also a growing number of smart building technologies, such as advanced building automation systems, IoT, and energy management systems, available, which can be used to better control how much energy is being consumed, and therefore optimise the operation of these buildings. Finally, increasing national and corporate-level commitment to net-zero and climate resilience strategies has created an increased demand for comprehensive and performance-based solutions; consequently, there is a higher likelihood of energy efficiency products (high-efficiency materials, renewable energy, etc.), energy performance benchmarking frameworks, and other similar solutions being utilised in both new and existing buildings.
Middle East Energy Efficient Buildings Market Report Coverage
|
Report Metric |
Details |
|
Historical Period |
2020 - 2024 |
|
Base Year Considered |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026 - 2035 |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 715.4 Million |
|
Revenue Forecast in 2035 |
USD 3203.9 Million |
|
Growth Rate |
15.6% |
|
Segments Covered in the Report |
Building Type, Technology, Application, End User, Material |
|
Report Scope |
Market Trends, Drivers, and Restraints; Revenue Estimation and Forecast; Segmentation Analysis; Companies’ Strategic Developments; Market Share Analysis of Key Players; Company Profiling |
|
Regions Covered in the Report |
Saudi Arabia, UAE |
|
Key Companies |
Saint‑Gobain, Johnson Controls, Honeywell International Inc., Schneider Electric, Siemens AG, Trane Technologies, Daikin Middle East & Africa, ENGIE Solutions Middle East, Etihad Energy Services (Etihad ESCO), Abu Dhabi Energy Services (ADES), Voltas Limited, Gulf Glass Industries, The National Mineral Wool Services Company (Tarshid / NESCO), Al‑Futtaim Engineering & Technologies (AFET), Design & Build Group |
|
Customization |
Available upon request |
Middle East Energy Efficient Buildings Market Segmentation
By Building Type
Residential buildings held the largest market share for approximately 55% of total market revenue in 2025. due to increased construction activity, an increasing number of urban residents, growing homeowner interest in cost savings related to reduced energy consumption, and a general cultural desire in many extreme climate locations for energy-efficient controlled indoor temperatures. As a result, energy performance upgrades for homes (i.e., smart controls, high-performance insulation) represent necessary investments for homeowners. Additionally, government policies that promote standards for energy-efficient housing and provide economic incentives for the development of “green” homes enhance the demand for energy efficiency upgrades in residential building applications over other potential applications, as According to the International Energy Agency, households accounted for 60% of total energy efficiency investment in 2024 including 70% of buildings-sector spending.
Commercial buildings are the fastest-growing category at a CAGR of 15.8% during the forecast period. This is because of corporate commitments to sustainability, tighter energy codes, and investor interest in reducing operational costs. The office building sector, retail center sector, and hospitality sector have increased their use of advanced energy management and controls for retrofits and integration into existing facilities, primarily due to tenant requests for sustainable space and an increasing number of ESG (environmental, social and governance) compliance requirements that make energy performance a strategic priority, with over 56 million gross square meters of commercial space certified under green building standards in 2024, indicating expanding adoption of sustainable commercial infrastructure.
By Technology
HVAC controls and equipment remain the largest technology with a market share of around 30% in 2025. This is due to the need for strong heating, ventilation, and cooling in the region to combat harsh climate conditions. HVAC systems are an important part of how energy is used, as they provide the necessary elements to support both indoor air quality and building comfort. With HVAC being a fundamental element of energy usage in commercial buildings, HVAC upgrades that utilize efficiency design will continue to be a priority for building owners and developers that want to measure improvements in reduced utility expenditures and enhanced occupant experience, as According to the International Energy Agency, global electricity consumption increased by 4.3% in 2024 largely due to higher cooling demand.
Energy management systems (EMS) are the fastest-growing technology at a CAGR of 15.8% in the coming years. This is because organizations want to be able to see in real time what is happening within their buildings through the use of data analytics, automation, and the ability to monitor and control multiple zones. The need for organizations to understand how they consume resources and have access to data so that they can better manage their facilities is driving organizations to deploy EMS. In addition to managing how they consume resources, organizations are also looking for ways to comply with regulations and meet their corporate sustainability goals, which will drive demand for smart energy solutions, as According to the International Energy Agency, building-sector efficiency investment reached approximately USD 225 billion in 2024 reflecting adoption of digital energy controls.
By Application
New construction represented the largest category with an estimated 45% share in 2025 due to urban growth and infrastructure development projects continuing to utilize energy efficiency design principles at every stage of a project. Since energy efficiency features are integrated into design, this provides maximum lifecycle performance benefits, and national development plans require or provide incentives for increased performance levels on all newly constructed assets, with buildings accounting for nearly 60% of global electricity consumption growth in 2024 highlighting the need for high-efficiency design integration.
Renovation and retrofitting are the fastest-growing application with a CAGR of 15.9% during the forecast period, because there is an increasing focus on upgrading the performance of existing buildings in order to meet changing code requirements and owner expectations. Retrofitting provides many benefits to stakeholders by allowing them to increase the useful life of their assets, decrease operating costs, and meet sustainability goals without having to fully redevelop the property, which makes it attractive for owners with large commercial or institutional portfolios, as According to the International Energy Agency, efficiency investment increased 4% to USD 660 billion in 2024 largely supporting building retrofits.
By End User
Residential property developers are the largest end-user with a market share of about 50% in 2025. It is due to their ability to include many energy-efficient design options as standard features in new home development so that they can enhance asset attractiveness and provide long-term value. Government direction on reducing utility costs through energy efficiency and consumers’ preference to reduce their utility bills have resulted in steady demand for optimized residential design and construction systems focused on energy efficiency, as According to the UN Environment Programme, the buildings and construction sector decoupled growth from emissions in 2024 due to widespread adoption of efficient design practices.
Commercial and office infrastructure end users are the fastest-growing category as a result of mandatory reporting requirements from corporate clients and tenants demanding energy-responsive spaces. The use of advanced technologies, high-efficiency products, and the development of performance benchmarks in commercial buildings will be driven by this customer base, with more than 170 organisations and governments committed to net-zero carbon buildings by 2024 reflecting rising demand for low-carbon office infrastructure.
By Material
Glass wool and mineral wool materials dominate because of their thermal insulation, fire resistance, and acoustic properties, which make them suitable for large-scale use across residential and commercial construction. Their ability to perform well in extreme temperatures allows glass wool and mineral wool to be used in a wide variety of building types.
Polyurethane products have the fastest growth rate with a CAGR of 16.2% during the forecast period, as advancements in compound formulation and installation techniques allow for higher-performing materials that meet current and future building code requirements. Polyurethane products are increasingly selected for retrofit projects and new construction with the goal of achieving maximum thermal performance.
Regional Insights
Middle East Energy Efficient Buildings Market
The Middle East has a very unique set of challenges, from the climate to the urbanisation of the region, to the commitment of many of these nations to sustainability, that drive the Middle East's energy efficiency building market as a whole and create some very different regional drivers. In addition, high levels of energy consumption in this hot and often desert climate, combined with the aggressive national goals of reducing carbon footprint through the implementation of new building codes, green certifications, and performance-based design practices focused on building design and operation for thermal efficiency and operational sustainability, have all created an environment that will support increased adoption of energy efficiency across the entire spectrum of the Middle East building stock (residential, commercial, and institutional). This same environment, which supports such large-scale and long-term energy efficiency adoption across the various sectors of the Middle East building stock, also creates a very similar environment that will support the long-term growth of the Middle East energy efficiency building market. Furthermore, there is increasing alignment between public and private sector stakeholders around smart city development and infrastructure modernisation initiatives, including the integration of advanced materials, automated energy management systems, and retrofit programs into broad development agendas.
Saudi Arabia Middle East Energy Efficient Buildings Market
The Saudi Arabian market is based on several factors, such as the country's "Vision 2030," which is a set of sustainability policies for the country, the building code requirements (which are strict), and large-scale urban renewal projects to incorporate energy performance standards. All of these have led to the demand for energy-efficient building products within both the residential and commercial markets due to rapid urbanisation, economic incentives by the government, and growing public awareness of operating energy costs.
UAE Middle East Energy Efficient Buildings Market
The UAE has an increasingly competitive market for energy-efficient buildings through both national strategies to develop sustainable environments and regulatory requirements for companies to implement green building and performance standards. In addition, high-profile smart city developments, along with corporate ESG commitments, have increased interest in integrated energy systems to support development of the UAE's role as a leader in growth and innovation for sustainable construction and energy efficiency, as According to the Dubai Supreme Council of Energy, cumulative electricity savings reached 13 TWh in 2024 through building retrofit and demand-side management initiatives.
Competitive Landscape / Company Insights
The Middle East energy-efficient buildings market is fragmented. That is, there are many different manufacturers and suppliers of various products, technologies, and services within this region; therefore, it does not have a few major players as do other markets, such as the U.S. and Europe. The diversity of the competitive landscape can be attributed to the large number of products and technologies available in the energy efficiency marketplace, including insulation materials, high-efficiency systems (such as HVAC), and integrated control platforms, which include both domestic and foreign companies providing products and solutions to meet the requirements of each country's building codes and priorities. Suppliers of products and technologies compete primarily based on product performance characteristics and how well their product or technology integrates with other products and services being used in the building. In addition, they also differentiate themselves based on services provided at the local level (i.e., service offerings and support).
Partnerships and joint ventures are common among suppliers of products and technologies in the energy efficiency marketplace. Distributors of products and technologies throughout the region also provide additional competitive pressure. Furthermore, the degree of regulatory compliance, size of projects, and type of customer needs vary greatly among the countries of the GCC and the wider Middle Eastern region. These variations create a dispersed distribution of market influence among competitors and do not allow for concentration of market power in one or two organizations.
Mini Profiles
Saint-Gobain Global building materials leader specialising in insulation, glass, and energy-efficient construction solutions, serving residential, commercial, and industrial projects across the Middle East with sustainable, high-performance building products.
Johnson Controls Multinational provider of HVAC, energy management, and building automation systems, delivering solutions for commercial, institutional, and industrial facilities to optimise energy efficiency and operational performance in the Middle East.
Honeywell International Inc. Technology and engineering company offering building automation, HVAC controls, and energy management solutions, serving commercial and industrial customers seeking sustainable and efficient building operations across the region.
Schneider Electric Global specialist in energy management and automation, providing smart building systems, energy-efficient infrastructure, and integrated controls for commercial, institutional, and industrial sectors in the Middle East.
Siemens AG International industrial and technology corporation supplying building technologies, energy-efficient solutions, and intelligent control systems for commercial, industrial, and infrastructure projects across Middle Eastern markets.
Key Players
- Saint Gobain
- Johnson Controls
- Honeywell International Inc.
- Schneider Electric
- Siemens AG
- Trane Technologies
- Daikin Middle East & Africa
- ENGIE Solutions Middle East
- Etihad Energy Services (Etihad ESCO)
- Abu Dhabi Energy Services (ADES)
- Voltas Limited
- Gulf Glass Industries
- The National Mineral Wool Services Company (Tarshid/ NESCO)
- Al‑Futtaim Engineering & Technologies (AFET)
- Design & Build Group
Recent Developments
January 2026 - Engie reached financial close on the Khazna solar park project in Abu Dhabi, enabling construction of a large-scale renewable power facility in partnership with Masdar under a long-term power supply agreement.
October 2025 - Masdar and consortium partners were awarded five major renewable energy projects in Saudi Arabia, marking contract wins under the country’s sustainable energy expansion plans.
March 2025 - Técnicas Reunidas secured a major engineering and construction contract with Orascom to expand a combined-cycle power plant in Saudi Arabia, including carbon capture infrastructure and an electrical substation, strengthening its presence in regional energy infrastructure.
Middle East Energy Efficient Buildings Market Coverage
Building Type Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
- Institutional
Technology Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- Energy Management Systems
- HVAC Controls & Equipment
- Lighting & Fixtures
- Building Envelope & Insulation Materials
- Renewable Energy Integration
Application Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- New Construction
- Renovation & Retrofitting
- Maintenance & Upgrades
End User Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- Residential Property Developers
- Commercial & Office Infrastructure
- Institutional & Government Projects
- Industrial Facilities
Material Insight and Forecast 2026 - 2035
- Glass Wool & Mineral Wool
- Expanded & Extruded Polystyrene
- Polyurethane
- Others
Middle East Energy Efficient Buildings Market by Region
- Saudi Arabia
- By Building Type
- By Technology
- By Application
- By End User
- By Material
- UAE
- By Building Type
- By Technology
- By Application
- By End User
- By Material
Table of Contents for Middle East Energy Efficient Buildings Market Report
1. Research Overview
1.1. The Report Offers
1.2. Market Coverage
1.2.1. By
Building Type
1.2.2. By
Technology
1.2.3. By
Application
1.2.4. By
End User
1.2.5. By
Material
1.3. Research Phases
1.4. Limitations
1.5. Market Methodology
1.5.1. Data Sources
1.5.1.1.
Primary Research
1.5.1.2.
Secondary Research
1.5.2. Methodology
1.5.2.1.
Data Exploration
1.5.2.2.
Forecast Parameters
1.5.2.3.
Data Validation
1.5.2.4.
Assumptions
1.5.3. Study Period & Data Reporting Unit
2. Executive Summary
3. Industry Overview
3.1. Industry Dynamics
3.1.1. Market Growth Drivers
3.1.2. Market Restraints
3.1.3. Key Market Trends
3.1.4. Major Opportunities
3.2. Industry Ecosystem
3.2.1. Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
3.2.2. Recent Development Analysis
3.2.3. Value Chain Analysis
3.3. Competitive Insight
3.3.1. Competitive Position of Industry
Players
3.3.2. Market Attractive Analysis
3.3.3. Market Share Analysis
4. Middle Market Estimate and Forecast
4.1. Middle Market Overview
4.2. Middle Market Estimate and Forecast to 2035
5. Market Segmentation Estimate and Forecast
5.1. By Building Type
5.1.1. Residential
5.1.1.1. Market Definition
5.1.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.1.2. Commercial
5.1.2.1. Market Definition
5.1.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.1.3. Industrial
5.1.3.1. Market Definition
5.1.3.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.1.4. Institutional
5.1.4.1. Market Definition
5.1.4.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.2. By Technology
5.2.1. Energy Management Systems
5.2.1.1. Market Definition
5.2.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.2.2. HVAC Controls & Equipment
5.2.2.1. Market Definition
5.2.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.2.3. Lighting & Fixtures
5.2.3.1. Market Definition
5.2.3.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.2.4. Building Envelope & Insulation Materials
5.2.4.1. Market Definition
5.2.4.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.2.5. Renewable Energy Integration
5.2.5.1. Market Definition
5.2.5.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.3. By Application
5.3.1. New Construction
5.3.1.1. Market Definition
5.3.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.3.2. Renovation & Retrofitting
5.3.2.1. Market Definition
5.3.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.3.3. Maintenance & Upgrades
5.3.3.1. Market Definition
5.3.3.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.4. By End User
5.4.1. Residential Property Developers
5.4.1.1. Market Definition
5.4.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.4.2. Commercial & Office Infrastructure
5.4.2.1. Market Definition
5.4.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.4.3. Institutional & Government Projects
5.4.3.1. Market Definition
5.4.3.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.4.4. Industrial Facilities
5.4.4.1. Market Definition
5.4.4.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.5. By Material
5.5.1. Glass Wool & Mineral Wool
5.5.1.1. Market Definition
5.5.1.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.5.2. Expanded & Extruded Polystyrene
5.5.2.1. Market Definition
5.5.2.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.5.3. Polyurethane
5.5.3.1. Market Definition
5.5.3.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
5.5.4. Others
5.5.4.1. Market Definition
5.5.4.2. Market Estimation and Forecast to 2035
6. Saudi Arabia Market Estimate and Forecast
6.1. By
Building Type
6.2. By
Technology
6.3. By
Application
6.4. By
End User
6.5. By
Material
7. UAE Market Estimate and Forecast
7.1. By
Building Type
7.2. By
Technology
7.3. By
Application
7.4. By
End User
7.5. By
Material
8. Company Profiles
8.1.
Saint?Gobain
8.1.1.
Snapshot
8.1.2.
Overview
8.1.3.
Offerings
8.1.4.
Financial
Insight
8.1.5.
Recent
Developments
8.2.
Johnson Controls
8.2.1.
Snapshot
8.2.2.
Overview
8.2.3.
Offerings
8.2.4.
Financial
Insight
8.2.5.
Recent
Developments
8.3.
Honeywell International Inc.
8.3.1.
Snapshot
8.3.2.
Overview
8.3.3.
Offerings
8.3.4.
Financial
Insight
8.3.5.
Recent
Developments
8.4.
Schneider Electric
8.4.1.
Snapshot
8.4.2.
Overview
8.4.3.
Offerings
8.4.4.
Financial
Insight
8.4.5.
Recent
Developments
8.5.
Siemens AG
8.5.1.
Snapshot
8.5.2.
Overview
8.5.3.
Offerings
8.5.4.
Financial
Insight
8.5.5.
Recent
Developments
8.6.
Trane Technologies
8.6.1.
Snapshot
8.6.2.
Overview
8.6.3.
Offerings
8.6.4.
Financial
Insight
8.6.5.
Recent
Developments
8.7.
Daikin Middle East & Africa
8.7.1.
Snapshot
8.7.2.
Overview
8.7.3.
Offerings
8.7.4.
Financial
Insight
8.7.5.
Recent
Developments
8.8.
ENGIE Solutions Middle East
8.8.1.
Snapshot
8.8.2.
Overview
8.8.3.
Offerings
8.8.4.
Financial
Insight
8.8.5.
Recent
Developments
8.9.
Etihad Energy Services (Etihad ESCO)
8.9.1.
Snapshot
8.9.2.
Overview
8.9.3.
Offerings
8.9.4.
Financial
Insight
8.9.5.
Recent
Developments
8.10.
Abu Dhabi Energy Services (ADES)
8.10.1.
Snapshot
8.10.2.
Overview
8.10.3.
Offerings
8.10.4.
Financial
Insight
8.10.5.
Recent
Developments
8.11.
Voltas Limited
8.11.1.
Snapshot
8.11.2.
Overview
8.11.3.
Offerings
8.11.4.
Financial
Insight
8.11.5.
Recent
Developments
8.12.
Gulf Glass Industries
8.12.1.
Snapshot
8.12.2.
Overview
8.12.3.
Offerings
8.12.4.
Financial
Insight
8.12.5.
Recent
Developments
8.13.
The National Mineral Wool Services Company (Tarshid / NESCO)
8.13.1.
Snapshot
8.13.2.
Overview
8.13.3.
Offerings
8.13.4.
Financial
Insight
8.13.5.
Recent
Developments
8.14.
Al?Futtaim Engineering & Technologies (AFET)
8.14.1.
Snapshot
8.14.2.
Overview
8.14.3.
Offerings
8.14.4.
Financial
Insight
8.14.5.
Recent
Developments
8.15.
Design & Build Group
8.15.1.
Snapshot
8.15.2.
Overview
8.15.3.
Offerings
8.15.4.
Financial
Insight
8.15.5.
Recent
Developments
9. Appendix
9.1. Exchange Rates
9.2. Abbreviations
Note: Financial insight and recent developments of different companies are subject to the availability of information in the secondary domain.
Frequently Asked Questions
Purchase Options
Latest Report
Research Methodology
- Desk Research / Pilot Interviews
- Build Market Size Model
- Research and Analysis
- Final Deliverable
Connect With Our Sales Team
- Toll-Free: +1-888-253-3960
- Phone: +91 9960 288 381
- Email: enquiry@vynzresearch.com
Middle East Energy Efficient Buildings Market
